Topic 1: Exam Set A
A technician has several possible solutions to a reported server issue. Which of the following BEST represents how the technician should proceed with troubleshooting?
A. Determine whether there is a common element in the symptoms causing multiple problems.
B. Perform a root cause analysis.
C. Make one change at a time and test.
D. Document the findings, actions, and outcomes throughout the process.
Explanation:
C. Make one change at a time and test is the best representation of how to proceed when the technician has already identified several possible solutions. This is a fundamental principle of effective troubleshooting.
Why it's the best:
When multiple potential solutions are on the table, implementing them simultaneously creates ambiguity. If the problem is resolved, you won't know which change fixed it. If the problem gets worse, you won't know which change caused the new issue. By making one change and then testing the result, the technician can definitively identify the solution that works. This method is systematic, minimizes risk, and prevents the introduction of new, unknown variables.
Why the other options are important, but not the best next step in this specific scenario:
A. Determine whether there is a common element in the symptoms causing multiple problems.
This is an excellent step in the problem identification and theory formation stages of troubleshooting. However, the question states the technician already has "several possible solutions," meaning this diagnostic analysis has likely already been performed. The question is asking how to proceed with those solutions.
B. Perform a root cause analysis.
Root cause analysis is a high-level, formal process undertaken after an incident is resolved to prevent its recurrence. It is the final step in a major incident review, not the immediate action for testing potential fixes during active troubleshooting.
D. Document the findings, actions, and outcomes throughout the process.
Documentation is a critical and continuous best practice that should happen during all stages of troubleshooting. However, it is a supporting process, not the primary methodology for testing solutions. The core action of "how to proceed" with the fixes is to implement them one at a time, and documentation records that process.
Reference:
This question aligns directly with CompTIA's established troubleshooting methodology, which is a core part of all their certifications, including Server+ (SK0-005 Objective 6.1, "Explain the troubleshooting theory and methodology"). The standard steps are:
Identify the problem.
Establish a theory of probable cause.
Test the theory to determine the cause.
Establish a plan of action to resolve the problem and implement the solution.
Verify full system functionality.
Document the findings, actions, and outcomes.
Option C is the practical application of steps 3 and 4. Making one change at a time is the only way to test a theory definitively.
Following a recent power outage, a server in the datacenter has been constantly going offline and losing its configuration. Users have been experiencing access issues while using the application on the server. The server technician notices the data and time are incorrect when the server is online. All other servers are working. Which of the following would MOST likely cause this issue? (Choose two.)
A. The server has a faulty power supply
B. The server has a CMOS battery failure
C. The server requires OS updates
D. The server has a malfunctioning LED panel
E. The servers do not have NTP configured
F. The time synchronization service is disabled on the servers
F. The time synchronization service is disabled on the servers
Explanation:
The issue described — a server losing its configuration and showing an incorrect date and time after power outages — points to problems with hardware timekeeping and time synchronization services.
B. The server has a CMOS battery failure
The CMOS battery stores BIOS/UEFI settings, including system date and time.
If it fails, the server forgets these settings each time it loses power, causing boot issues, incorrect timestamps, and sometimes network authentication failures (since time-sensitive certificates can become invalid).
F. The time synchronization service is disabled on the servers
Even if the CMOS battery fails, a properly configured NTP (Network Time Protocol) or time synchronization service can automatically correct the clock when the system comes online.
If this service is disabled, the server clock remains incorrect, leading to access and authentication errors for users.
Why the Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Faulty power supply:
Would cause boot or power instability, but not time loss or configuration resets after every reboot.
C. OS updates required:
Missing updates wouldn’t cause clock resets or configuration loss after power outages.
D. Malfunctioning LED panel:
Cosmetic issue only — unrelated to server performance or configuration.
E. Servers do not have NTP configured:
While possible, the question specifies the issue affects one server only, and all other servers are functioning properly — so NTP configuration is not the cause.
Reference:
CompTIA Server+ SK0-005 Exam Objectives, Domain 4.2: “Given a scenario, apply server troubleshooting methodologies.”
NIST SP 800-88: Guidelines for Time Synchronization and CMOS Maintenance
Microsoft Docs: Windows Time Service Tools and Settings
In summary:
The problem is due to a CMOS battery failure (B) and a disabled time synchronization service (F) — causing time drift and loss of configuration after power loss.
Which of the following should an administrator use to transfer log files from a Linux server to a Windows workstation?
A. Telnet
B. Robocopy
C. XCOPY
D. SCP
Explanation
SCP (Secure Copy Protocol) is the MOST appropriate choice for transferring files from a Linux server to a Windows workstation, especially for sensitive data like log files.
Security:
SCP operates over the SSH (Secure Shell) protocol. This means the file transfer is fully encrypted, which is essential for transferring log files that may contain sensitive system or user information.
Cross-Platform Support:
SCP is a native and standard utility on virtually all Linux and Unix-like operating systems. On the Windows side, it can be used easily via modern Windows PowerShell/CMD (if OpenSSH is installed), or through popular third-party clients like WinSCP or PuTTY's pscp utility.
Command-Line Utility:
As a command-line tool, it is ideal for administrators who need to script or automate the log file transfer process.
Why the Other Options are Incorrect
A. Telnet:
Telnet is an old, unencrypted protocol used for remote terminal access. It is not a file transfer protocol and should never be used for moving data due to the lack of security.
B. Robocopy:
Robocopy (Robust File Copy) is a powerful utility native to Microsoft Windows (Windows Server, Windows 10/11) used for copying files and directories. It is not installed or natively compatible with Linux to initiate a copy from the Linux server to the Windows machine without setting up an intermediate protocol like SMB/CIFS, which is less direct than SCP.
C. XCOPY:
XCOPY is an older, basic file-copy command native to Microsoft Windows. Like Robocopy, it is not a protocol for transferring files across different operating systems like Linux over a network.
Reference
CompTIA Server+ SK0-005 Exam Objectives
3.3 – Given a scenario, use remote access methods
→ Includes SCP as a secure file transfer method over SSH.
A server administrator needs to check remotely for unnecessary running services across 12 servers. Which of the following tools should the administrator use?
A. DLP
B. A port scanner
C. Anti-malware
D. A sniffer
Explanation:
B. A port scanner is the correct tool for this task.
A port scanner is a network tool designed to probe a server or host for open ports.
How it works:
Each network service (e.g., web server, file sharing, remote desktop) listens for connections on a specific port number (e.g., port 80 for HTTP, port 22 for SSH). By scanning the servers remotely, the administrator can get a list of all open ports on each machine.
Identifying Unnecessary Services:
The administrator can then compare the list of open ports against a known baseline or documentation to identify services that are running and listening for connections but are not required for the server's function. An open port is a strong indicator of a running service.
Why the other options are incorrect:
A. DLP (Data Loss Prevention):
This is a security solution focused on monitoring, detecting, and blocking sensitive data from leaving an organization. It is not a tool for discovering what network services are running on a server.
C. Anti-malware:
This software is designed to prevent, detect, and remove malicious software (viruses, worms, trojans, etc.). While some unnecessary services could be a security risk, anti-malware tools are not designed to perform a comprehensive inventory of all running network services across multiple servers.
D. A sniffer (Protocol Analyzer):
A sniffer, like Wireshark, captures and analyzes network traffic passing through a network segment. It is excellent for troubleshooting network communication problems or analyzing the content of traffic to and from a service. However, it is a passive tool that monitors traffic flow; it does not actively probe servers to see which ports are open. If a service isn't receiving any traffic, a sniffer might not see it, whereas a port scanner will actively find it.
Reference:
This task falls under CompTIA Server+ SK0-005 Objective 2.2, "Given a scenario, configure servers to use network infrastructure services," and general security hardening practices. Part of server hardening is to disable any unnecessary services to reduce the attack surface. A port scanner is the standard tool for remotely auditing which network services are exposed.
Users in an office lost access to a file server following a short power outage. The server administrator noticed the server was powered off. Which of the following should the administrator do to prevent this situation in the future?
A. Connect the server to a KVM
B. Use cable management
C. Connect the server to a redundant network
D. Connect the server to a UPS
Explanation:
A UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) provides temporary backup power during short power outages or voltage drops.
If the file server shut down when the power failed, it likely wasn’t connected to a UPS. By connecting it to one, the server can stay online long enough for the power to return or to perform a graceful shutdown, preventing downtime and data loss.
UPS systems also protect against power surges and fluctuations, improving the overall reliability of the server.
Why the Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Connect the server to a KVM:
A KVM switch allows multiple servers to be controlled from one keyboard, video, and mouse setup. It doesn’t provide power backup or protection.
B. Use cable management:
Helps with organization and airflow but does nothing to prevent power loss or outages.
C. Connect the server to a redundant network:
Improves network availability, not power availability. Network redundancy doesn’t keep the server running during a power outage.
Reference:
CompTIA Server+ SK0-005 Exam Objectives, Domain 4.3: “Explain disaster recovery and power protection methods.”
NIST SP 800-94: Guide to Intrusion Detection and Power System Protection
In summary:
To prevent shutdowns during power outages, the server should be connected to a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply).
Which of the following would MOST likely be part of the user authentication process when implementing SAML across multiple applications?
A. SSO
B. LDAP
C. TACACS
D. MFA
Explanation
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) is an XML-based standard used to exchange authentication and authorization data between an Identity Provider (IdP) and Service Providers (SPs) — typically to enable Single Sign-On (SSO) across multiple applications.
SSO is the core purpose of SAML:
User authenticates once to the IdP (e.g., Okta, Azure AD, Ping Identity).
IdP issues a SAML assertion (token).
User accesses multiple applications without re-logging in.
Thus, SSO is the most likely component of the user authentication process when implementing SAML.
Why the others are not correct:
B. LDAP
Used for directory lookups (e.g., user attributes). Can be a backend to the IdP, but not part of the SAML exchange itself.
C. TACACS
Cisco protocol for device administration (AAA), not web/application SSO. No relation to SAML.
D. MFA
Enhances initial authentication at the IdP. It may be used before SAML assertion is issued, but MFA is not part of the SAML protocol — it’s an optional pre-step.
Reference
CompTIA Server+ SK0-005 Exam Objectives
5.3 – Explain the role of authentication and authorization in security
→ Includes SAML and SSO as federation/authentication methods.
Final Answer: A. SSO
It is the primary outcome and integral part of implementing SAML across applications.
Users have noticed a server is performing below Baseline expectations. While diagnosing me server, an administrator discovers disk drive performance has degraded. The administrator checks the diagnostics on the RAID controller and sees the battery on me controller has gone bad. Which of the following is causing the poor performance on the RAID array?
A. The controller has disabled the write cache.
B. The controller cannot use all the available channels.
C. The drive array is corrupt.
D. The controller has lost its configuration.
Explanation:
A. The controller has disabled the write cache. This is the correct and most direct cause of the performance degradation.
Role of the Battery:
The battery (or flash-backed write cache - BBWC/FBWC) on a RAID controller is a critical component. Its primary job is to protect data in the controller's volatile write cache in the event of a power failure. It provides enough power to flush the contents of the cache down to the non-volatile drives, ensuring no data in transit is lost.
Fail-Safe Behavior:
When the controller's battery fails or is discharged, it enters a fail-safe mode. To prevent data loss (since it can no longer guarantee the safety of cached writes), the controller will automatically disable the write-back cache and revert to a much slower write-through cache mode.
Performance Impact:
In write-back cache mode, the controller acknowledges a write operation as soon as the data is in its fast cache, before it's physically written to the disks. This is very fast. In write-through mode, the controller must wait for the data to be physically written to the slower disks before acknowledging the write, which causes a significant performance penalty, exactly matching the symptom of "degraded disk drive performance."
Why the other options are incorrect:
B. The controller cannot use all the available channels.
A failed battery does not affect the physical data channels between the controller and the drives. The drives are still connected and communicating.
C. The drive array is corrupt.
A bad battery does not cause corruption. In fact, its fail-safe behavior of disabling the cache is specifically designed to prevent corruption by ensuring all writes are committed to disk immediately. The array should be intact, just slow.
D. The controller has lost its configuration.
The RAID configuration is stored in non-volatile memory (NVRAM) on the controller, not maintained by the battery. A bad battery will not cause the controller to lose its configuration.
Reference:
This is a classic scenario covered under CompTIA Server+ SK0-005 Objective 3.1, "Given a scenario, perform server hardware maintenance," and general storage administration knowledge. Understanding the critical role of the RAID controller cache and its battery is essential for troubleshooting performance issues in high-end servers. Replacing a failed battery is a standard maintenance task to restore performance.
A server has experienced several component failures. To minimize downtime, the server administrator wants to replace the components while the server is running. Which of the following can MOST likely be swapped out while the server is still running? (Select TWO).
A. The power supply
B. The CPU
C. The hard drive
D. The GPU
E. The cache
F. The RAM
C. The hard drive
Explanation:
Many enterprise-grade servers are designed with hot-swappable components — parts that can be replaced without shutting down the system.
The most common hot-swappable components are power supplies and storage drives, as they’re built for redundancy and continuous uptime.
A. The power supply
Enterprise servers often have redundant power supplies.
If one fails, the other continues to provide power, allowing the faulty unit to be replaced while the server is still running — ensuring no downtime.
C. The hard drive
In servers with RAID arrays or hot-swap drive bays, individual hard drives can also be replaced on the fly.
The array continues running using redundancy (like RAID 1, 5, or 6), and the replaced drive is automatically rebuilt after insertion.
Why the Other Options Are Incorrect:
B. The CPU:
Cannot be replaced while the server is powered on — requires full shutdown and reinstallation.
D. The GPU:
Not hot-swappable; removal under power could cause hardware damage.
E. The cache:
Integrated into the CPU or motherboard — not a removable or serviceable part.
F. The RAM:
Typically not hot-swappable unless using specialized systems that support memory hot-add (rare in standard servers).
Reference:
CompTIA Server+ SK0-005 Exam Objectives, Domain 4.2: “Given a scenario, apply server troubleshooting and maintenance procedures.”
Dell PowerEdge / HPE ProLiant Documentation: Hot-plug Power Supply and Hot-swap Drive Support.
NIST SP 800-94: High Availability and Redundancy Concepts.
In summary:
The components that can most likely be replaced while the server is running are the Power Supply (A) and Hard Drive (C).
Which of the following are measures that should be taken when a data breach occurs?
(Select TWO).
A. Restore the data from backup.
B. Disclose the incident.
C. Disable unnecessary ports.
D. Run an antivirus scan.
E. Identify the exploited vulnerability.
F. Move the data to a different location.
E. Identify the exploited vulnerability.
Explanation
B. Disclose the incident
This is a legal and ethical requirement in most jurisdictions (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, various state laws). Timely disclosure (or notification) must be made to regulatory bodies and, most importantly, the affected individuals.
It protects the affected individuals by giving them an opportunity to take mitigating steps (like changing passwords or setting up credit monitoring) and helps the organization manage its legal and reputational risk through transparency.
E. Identify the exploited vulnerability
This is a core component of the Eradication and Remediation phases of incident response. You must pinpoint the root cause (the hole the attacker used) to patch it and prevent the attacker from simply coming back the same way.
The system cannot be considered secure or brought back online until the exploited vulnerability is correctly identified and closed.
Analysis of Other Options
A. Restore the data from backup:
This is part of the Recovery phase, which comes after the breach has been contained, the threat has been eradicated, and the root cause (vulnerability) has been fixed. Restoring data before fixing the vulnerability just puts the clean data back onto a compromised system.
C. Disable unnecessary ports:
This is a good proactive security measure to prevent future breaches and can be a part of Containment (isolating the affected system), but it's not the primary, universally required step like Disclosure or identifying the exploit. The specific exploited vector might not have been an open port.
D. Run an antivirus scan:
This is a step in Eradication but is often insufficient, as advanced attacks bypass standard antivirus. The more crucial step is forensic analysis to find the root cause (E), not just surface-level malware.
F. Move the data to a different location:
This is generally ineffective and can hinder the forensic investigation. The focus should be on isolating (Containment) and securing the compromised environment, not just moving the data to another potentially insecure location.
Reference
CompTIA Server+ SK0-005 Exam Objectives
5.4 – Given a scenario, apply appropriate security controls for servers
→ Includes incident response procedures: identification, containment, disclosure, eradication.
NIST SP 800-61 – Computer Security Incident Handling Guide
Key steps: Detection → Analysis → Containment → Eradication → Recovery → Post-incident (including disclosure and lessons learned)
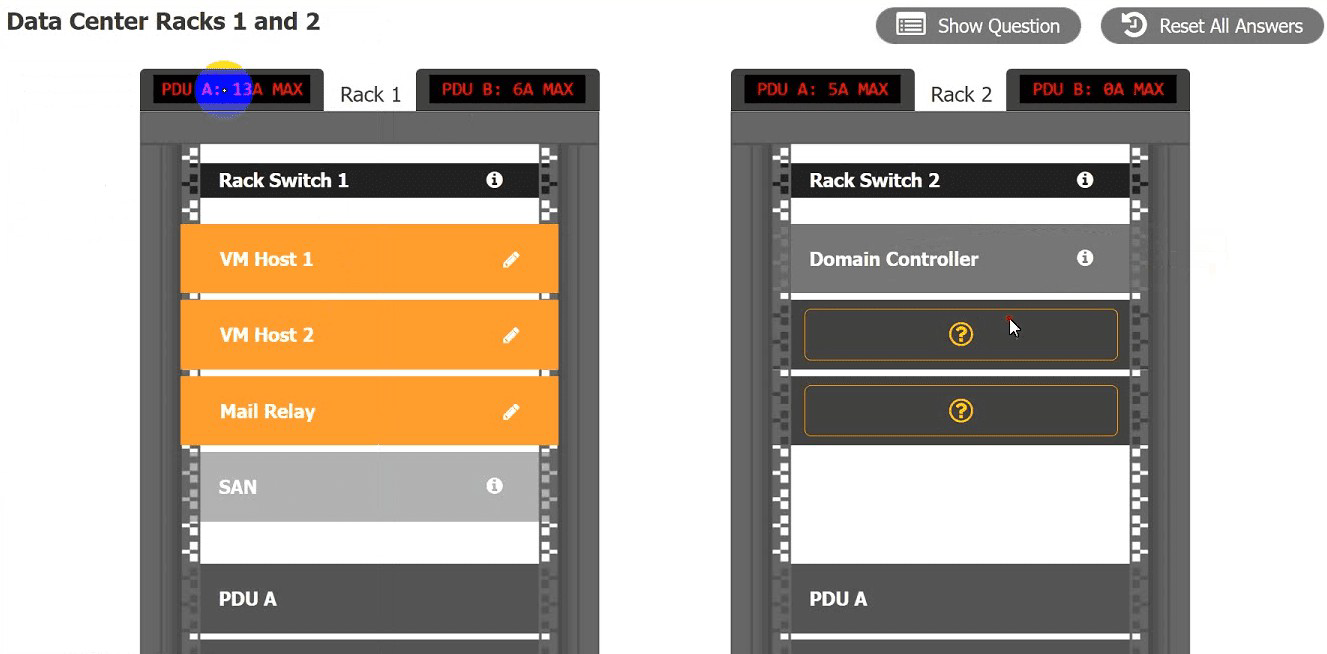
A recent power Outage caused email services to go down. A sever administrator also
received alerts from the datacenter’s UPS.
After some investigation, the server administrator learned that each POU was rated at a
maximum Of 12A.
INSTRUCTIONS
Ensure power redundancy is implemented throughout each rack and UPS alarms are
resolved. Ensure the maximum potential PDU consumption does not exceed 80% or 9.6A).
a. PDU selections must be changed using the pencil icon.
b. VM Hosts 1 and 2 and Mail Relay can be moved between racks.
c. Certain devices contain additional details
.png)
| Page 5 out of 50 Pages |
