Topic 1: Exam Set A
Which of me following BEST describes a disaster recovery site with a target storage array that receives replication traffic and servers that are only powered on In the event of a disaster?
A. Cloud
B. Cold
C. Hot
D. Warm
Explanation:
A warm site is a partially prepared disaster recovery (DR) location. It has pre-installed hardware, such as servers and storage systems, that receive replicated data from the primary site, but these servers are not powered on or active during normal operations.
In the event of a disaster, administrators can power on the servers, synchronize data, and bring systems online relatively quickly — faster than a cold site but slower than a hot site.
Why Others Are Incorrect:
A. Cloud:
Cloud DR can refer to any model (hot, warm, or cold) depending on configuration. The question specifically mentions replication and powered-on servers only during a disaster, which matches a warm site, not a general cloud setup.
B. Cold:
A cold site usually has no active hardware or data replication. Setup and restoration take a long time since all systems must be built and data restored from backups.
C. Hot:
A hot site is fully operational and synchronized in real-time. Servers are powered on and can take over immediately with minimal downtime — unlike the scenario described.
Reference:
CompTIA Server+ SK0-005 Exam Objectives, Domain 4.3: "Explain disaster recovery concepts and methods."
CompTIA Server+ Study Guide (Exam SK0-005), Chapter 10: Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity Planning – section on Hot, Warm, and Cold Sites.
In summary:
Replication traffic + servers powered on only during disaster = Warm Site
A server room with many racks of servers is managed remotely with occasional on-site support. Which of the following would be the MOST cost-effective option to administer and troubleshoot network problems locally on the servers?
A. Management port
B. Crash cart
C. IP KVM
D. KVM
Explanation
The question asks for the MOST cost-effective option to administer and troubleshoot servers locally (on-site, in the server room).
KVM (Keyboard, Video, Mouse) Switch:
A standard KVM switch is a single device installed in the rack that allows a technician to use one set of peripherals (keyboard, monitor, mouse) to control multiple servers.
Local Administration:
The peripherals are connected locally in the rack.
Cost-Effective:
It allows the one set of expensive console equipment to be shared among many servers, making it highly cost-effective per server, especially compared to buying an IP-enabled version or rolling around a complete crash cart for every occasional need.
Analysis of Incorrect Options:
A. Management port:
A management port (like an integrated Dell Remote Access Controller/iDRAC or HPE Integrated Lights-Out/iLO) is excellent for remote administration and troubleshooting, but it is not a local device that is used for direct on-site work with a monitor/keyboard. It also requires the network to be functional (unless using an out-of-band network).
B. Crash cart:
A crash cart is a physical, mobile cart containing a monitor, keyboard, and mouse that is wheeled up to the server rack. While it provides local access, it is generally considered less cost-effective than a fixed KVM switch because it involves more hardware (a dedicated monitor, keyboard, and mouse) that must be physically moved. Modern server rooms often use a fixed KVM or a small, portable KVM Crash Cart Adapter (which connects a laptop to the server's console port) in place of the older, large physical cart. However, a traditional, fixed KVM switch in the rack is the classic and most economical permanent local solution for multiple servers.
C. IP KVM (KVM over IP):
An IP KVM is an advanced KVM switch that adds the ability to access the console remotely over a network connection. This is significantly more expensive than a standard, local KVM switch and is overkill if the primary requirement is occasional local troubleshooting and administration.
CompTIA Server+ Context (SK0-005)
This question falls under Domain 1.0: Server Administration (specifically the tools used for management and troubleshooting). The key to the answer lies in balancing the requirements: local access and cost-effectiveness for many racks of servers. A centralized, non-IP KVM console in the rack is the traditional, most economical hardware solution for local control of multiple devices.
Reference:
CompTIA Server+ (SK0-005) study materials cover the use and comparison of KVMs, IP KVMs, and remote management tools for server access.
A server technician installs a new NIC on a server and configures the NIC for IP
connectivity. The technician then tests the connection using thepingcommand. Given the
following partial output of thepingandipconfigcommands:
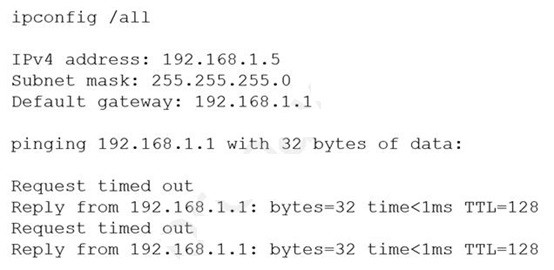
Which of the following caused the issue?
A. Duplicate IP address
B. Incorrect default gateway
C. DHCP misconfiguration
D. Incorrect routing table
Explanation:
The ping 10.20.10.15 command succeeds, and ipconfig shows the server’s IP is also 10.20.10.15. Pinging your own IP should only work via loopback — but getting real replies with TTL=128 and low latency means another device on the network is responding. This only happens with a duplicate IP address.
Why the other options are incorrect:
B. Incorrect default gateway
A wrong gateway prevents external network access, but local subnet pings (including self-ping via ARP) would still work. It does not cause successful replies from another device.
C. DHCP misconfiguration
The output shows a statically configured IP (ipconfig shows manual settings), not DHCP. Also, DHCP issues cause “no IP” or “APIPA (169.254.x.x)” — not duplicate responses.
D. Incorrect routing table
Routing affects inter-network traffic, not local subnet ARP or self-ping behavior. A bad route doesn’t cause duplicate IP responses.
Reference:
CompTIA Server+ SK0-005 Exam Objectives:
1.3 – Given a scenario, troubleshoot common network connectivity issues
Includes identifying duplicate IP addresses via ping behavior and ARP conflicts.
Microsoft Windows Behavior:
When a duplicate IP exists, Windows may log:
“The system detected an address conflict for IP address 10.20.10.15 with the system having network hardware address...”
(Event ID 4199 in System log)
Final Answer: A. Duplicate IP address
The successful ping to the server’s own IP from itself — when testing connectivity — indicates another device is responding, confirming a duplicate IP conflict.
Which of the following is a method that is used to prevent motor vehicles from getting too close to building entrances and exits?
A. Bollards
B. Reflective glass
C. Security guards
D. Security cameras
Explanation:
A. Bollards are the correct answer. Bollards are short, sturdy vertical posts made of steel, concrete, or other durable materials. They are installed in strategic locations, such as in front of building entrances, exits, and other vulnerable points.
Primary Function:
Their explicit purpose is to provide physical security and perimeter control by creating a protective barrier. They prevent vehicles from intentionally or accidentally ramming into or getting too close to a building, a practice known as vehicle-ramming protection.
Method of Operation:
They work by physically blocking the path of a vehicle, absorbing the impact, and stopping it from proceeding further.
Why the other options are incorrect:
B. Reflective glassis primarily used for privacy, energy efficiency (by reflecting sunlight), or aesthetics. It does not provide any physical barrier to stop a vehicle.
C. Security guards are a deterrent and responsive measure. A guard can monitor vehicle traffic and report suspicious activity, but they cannot physically stop a determined vehicle from approaching a building. Their method is observational and procedural, not physical blocking.
D. Security cameras are a detective and deterrent control. They record activity and can provide evidence after an incident has occurred, but they offer zero physical prevention against a moving vehicle.
Reference:
This aligns with CompTIA Server+ SK0-005 Objective 4.1, "Given a scenario, apply physical security methods to protect physical assets." The objective includes implementing physical access controls and barriers, of which bollards are a prime example for mitigating threats from vehicles.
Which of the following techniques can be configured on a server for network redundancy?
A. Clustering
B. Vitalizing
C. Cloning
D. Teaming
Explanation:
Network interface card (NIC) teaming — also known as link aggregation or bonding — is a network redundancy technique where multiple physical NICs on a server are combined into a single logical interface.
If one network link fails, traffic automatically fails over to another NIC, maintaining network connectivity and increasing both redundancy and throughput.
Why Others Are Incorrect:
A. Clustering:
Refers to multiple servers working together to provide application or service redundancy, not network interface redundancy.
(Example: failover clustering for databases or web servers.)
B. Vitalizing (likely meant Virtualizing):
Virtualization allows multiple VMs to run on a single host but doesn’t inherently provide network redundancy.
C. Cloning:
Creates a copy of a system or VM, useful for deployment or testing — not a redundancy or failover mechanism.
Reference:
CompTIA Server+ (SK0-005) Exam Objectives, Domain 2.2: "Configure network services and redundancy."
Microsoft Docs: NIC Teaming Overview
Red Hat Documentation: Network Bonding Explained
In summary:
NIC Teaming provides network redundancy and load balancing, making D. Teaming the correct answer
Which of the following documents would be useful when trying to restore IT infrastructure operations after a non-planned interruption?
A. Service-level agreement
B. Disaster recovery plan
C. Business impact analysis
D. Business continuity plan
Explanation
The key function described in the question is to "restore IT infrastructure operations" after an "interruption."
Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP):
Focus:
It is a detailed, technical document that focuses specifically on recovering and restoring the organization's critical IT systems and data (servers, network, applications) to a usable state after a disaster or unplanned outage.
Goal:
The explicit goal of a DRP is to minimize downtime and meet defined Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPOs).
Relevance:
This plan contains the step-by-step procedures used by the technical team to bring the failed IT infrastructure back online—the exact scenario described.
Analysis of Incorrect Options:
A. Service-level agreement (SLA):
This is a contract that defines the level of service (e.g., uptime, response time) a provider guarantees to a customer. It states what recovery targets must be met, but it is not the document that contains the technical how-to steps for the restoration process.
C. Business impact analysis (BIA):
This is a preliminary document that identifies the critical business functions and systems, assesses the impact of their loss, and determines the RTOs and RPOs. It informs the DRP and BCP, but it does not contain the actual restoration steps.
D. Business continuity plan (BCP):
This is the high-level, overarching plan that focuses on keeping the entire business (personnel, processes, facilities, etc.) operational during and after a disaster. The DRP is a subset of the BCP that focuses only on the technology (IT infrastructure) component. While the BCP is activated first to manage the crisis, the DRP is the specific document used by server administrators to perform the actual restoration of the IT infrastructure.
Reference:
CompTIA Server+ (SK0-005) emphasizes the distinction between BCP (business-focused, broader scope) and DRP (IT-focused, system restoration procedures).
A server administrator is testing a disaster recovery plan. The test involves creating a downtime scenario and taking the necessary steps. Which of the following testing methods is the administrator MOST likely performing?
A. Backup recovery
B. Simulated
C. Tabletop
D. Live failover
Explanation:
The scenario describes creating a downtime scenario and taking necessary steps without indicating real production impact or actual failover. This matches a simulated (parallel) test: systems are brought up in an isolated environment to mimic failure and recovery, validating the plan without disrupting live operations.
Why the other options are incorrect:
A. Backup recovery
This only tests restoring data from backups—a single component. It does not involve creating a full downtime scenario or executing the entire DR plan (e.g., failover, network redirection, application validation).
C. Tabletop
A discussion-based exercise where team members talk through the DR plan in a meeting. No systems are touched, no downtime is created, and no actual steps are executed. It’s valuable for awareness but not technical testing.
D. Live failover
This involves actual switchover to backup systems in production—real traffic is redirected, and real downtime occurs if recovery fails. It’s the most realistic but highest-risk method, typically done only after simulated tests succeed. The question says “testing,” not “executing in production.”
Reference:
CompTIA Server+ SK0-005 Exam Objectives
4.1 – Explain the importance of backup and restore procedures
Includes disaster recovery testing methods:
Tabletop: Discussion only
Simulated/Parallel: Full procedure in isolated environment
Live/Cutover: Real production failover
Industry standard: NIST SP 800-84 and ISO 22301 recommend simulated testing as a balance between realism and safety.
Final Answer: B. Simulated
The administrator is performing a hands-on recovery test in a safe environment, which defines a simulated disaster recovery test.
Which of the following, if properly configured, would prevent a user from installing an OS on a server? (Select TWO).
A. Administrator password
B. Group Policy Object
C. Root password
D. SELInux
E. Bootloader password
F. BIOS/UEFI password
F. BIOS/UEFI password
Explanation:
To prevent an operating system (OS) installation, you must block the ability to boot from anything other than the existing, authorized hard drive. The two methods that directly control the boot process are:
E. Bootloader password:
A bootloader (like GRUB on Linux or the Windows Boot Manager) is the first software that runs when a computer starts, and it is responsible for loading the OS. If a password is set on the bootloader, it prevents unauthorized users from:
Interrupting the default boot process.
Accessing the boot menu to select an alternative OS or a recovery image.
Passing boot parameters (e.g., booting into single-user mode on Linux or safe mode on Windows, which could be used to gain elevated privileges and initiate an OS reinstall).
F. BIOS/UEFI password:
The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) or its modern replacement, UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface), is the firmware that initializes the hardware when the server is powered on. Setting a password here provides a deeper level of control by preventing unauthorized users from:
Changing the boot order. This is the most critical function. An OS is typically installed by booting from a USB drive, DVD, or network (PXE). A BIOS/UEFI password stops someone from changing the boot priority to these devices, forcing the system to always boot from the internal hard drive.
Accessing the BIOS/UEFI setup utility altogether.
By combining these two passwords, you protect both the firmware settings (BIOS/UEFI) and the software that loads the OS (Bootloader), creating a robust barrier against unauthorized OS installation.
Why the other options are incorrect:
A. Administrator password and C. Root password:
These are OS-level passwords. They are essential for controlling access within the installed OS, but they are ineffective if a user can simply boot the server from an external OS installation media. The installer environment operates outside the control of the existing OS's user accounts.
B. Group Policy Object (GPO):
This is a feature of Microsoft Active Directory that controls the working environment for user accounts and computer accounts within a Windows OS. Like local admin passwords, it has no jurisdiction over the boot process before the OS loads.
D. SELinux (Security-Enhanced Linux):
This is a security module for Linux that provides a mechanism for supporting access control security policies, including mandatory access controls (MAC). It is designed to confine the actions of users and processes within a running OS. It does not prevent the server from booting from an external device to install a new OS.
Reference:
This question falls under CompTIA Server+ SK0-005 Objective 4.2, "Explain the importance of physical security measures." While often thought of as logical security, controlling the boot process is a fundamental physical security measure because anyone with physical access to the server can attempt to boot it from their own media. BIOS/UEFI and bootloader passwords are the primary defenses against this threat.
Which of the following open ports should be closed to secure the server properly? (Choose two.)
A. 21
B. 22
C. 23
D. 53
E. 443
F. 636
C. 23
Explanation:
To properly secure a server, you should close or block any insecure or unnecessary ports.
Port 21 (FTP) and Port 23 (Telnet) are both unsecured protocols that transmit data, including credentials, in clear text. Attackers can easily intercept this traffic, making these ports major security risks.
Port 21 – FTP:
Used for file transfers, but it sends usernames and passwords without encryption. Replace it with SFTP (Port 22) or FTPS (Port 990) for secure file transfer.
Port 23 – Telnet:
Used for remote command-line access, but also unencrypted. Replace it with SSH (Port 22), which encrypts all communication.
Why Not the Others:
22 (SSH):
Secure remote management — should stay open if used for administration.
53 (DNS):
Needed for domain name resolution — typically remains open.
443 (HTTPS):
Secure web traffic — must be open for secure websites.
636 (LDAPS):
Secure LDAP — used for encrypted directory services communication.
Reference:
CompTIA Server+ SK0-005 Exam Objectives, Domain 3.1: “Summarize security best practices for server installation and management.”
NIST SP 800-41 Rev.1 – Guidelines on Firewalls and Firewall Policy
In summary:
Close Ports 21 (FTP) and 23 (Telnet) because they use unencrypted communication, leaving the server vulnerable to attacks.
A server administrator was asked to build a storage array with the highest possible capacity. Which of the following RAID levels should the administrator choose?
A. RAID 0
B. RAID 1
C. RAID 5
D. RAID 6
Explanation:
The requirement is to build a storage array with the highest possible capacity, meaning the maximum usable storage space from the available disks. This depends entirely on how much disk space is lost to redundancy or parity.
Let’s compare each RAID level in terms of capacity efficiency (assuming n disks of equal size):
A. RAID 0 (Striping)
Data is striped across all disks with no mirroring or parity.
Usable capacity = n × disk size (e.g., 4 × 1 TB = 4 TB usable).
Overhead = 0% → 100% of total raw capacity is usable.
This is the only RAID level that provides full disk utilization, making it the clear winner for maximum capacity.
B. RAID 1 (Mirroring)
Data is duplicated on paired disks.
Usable capacity = 1 × disk size (e.g., 4 disks → only 2 disks worth of storage).
50% overhead — half the space is used for redundancy.
C. RAID 5 (Striping with Parity)
Data and parity are distributed across all disks.
Usable capacity = (n – 1) × disk size (e.g., 4 × 1 TB = 3 TB usable).
One disk equivalent is lost to parity.
D. RAID 6 (Striping with Double Parity)
Similar to RAID 5 but uses two parity blocks.
Usable capacity = (n – 2) × disk size (e.g., 4 × 1 TB = 2 TB usable).
Two disks equivalent lost — even lower capacity.
Only RAID 0 uses every byte of every disk for storage, delivering the absolute highest possible capacity.
Important Note:
While RAID 0 offers zero fault tolerance (a single disk failure destroys the entire array), the question does not mention reliability, redundancy, or data protection — it asks only for highest capacity. Therefore, RAID 0 is the correct and intended answer.
Reference:
CompTIA Server+ SK0-005 Exam Objectives
2.3 – Compare and contrast RAID levels and configurations
→ Explicitly lists:
RAID 0: Highest performance and capacity, no fault tolerance
RAID 1, 5, 6: Trade capacity for redundancy
Storage Industry Standard:
RAID 0 is universally recognized as the maximum-capacity configuration in hardware and software RAID controllers.
Final Answer: A. RAID 0
It provides 100% usable capacity with no space lost to redundancy, making it the only choice for the highest possible storage capacity.
| Page 3 out of 50 Pages |
