A Chief Information Security Officer wants to lock down the users' ability to change applications that are installed on their Windows systems. Which of the following is the best enterprise-level solution?
A. HIPS
B. GPO
C. Registry
D. DLP
Explanation:
GPO is the best enterprise-level solution to lock down users’ ability to change or install applications on Windows systems. Group Policy allows administrators to centrally configure and enforce security settings, such as restricting software installation via policies like “Restrict users from installing software” or “AppLocker” rules. HIPS (Host-based Intrusion Prevention System) detects and blocks malicious activities but doesn’t specifically manage application installation permissions. Registry modifications can restrict settings but are not scalable for enterprise environments. DLP (Data Loss Prevention) focuses on protecting data, not controlling application installations.
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ Study Guide (CS0-003), Chapter 2: Security Operations
A security audit for unsecured network services was conducted, and the following output
was generated:
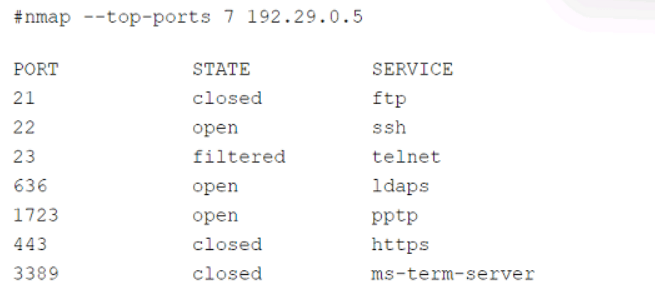
Which of the following services should the security team investigate further? (Select two).
A. 21
B. 22
C. 23
D. 636
E. 1723
F. 3389
D. 636
Explanation:
The security team should investigate services running on port 23 (Telnet) and port 3389 (RDP) further, as these are commonly associated with unsecured or high-risk network services:
Port 23 (Telnet):Telnet transmits data, including credentials, in plaintext, making it highly vulnerable to interception and unauthorized access. It’s considered insecure and should be replaced with secure alternatives like SSH.
Port 3389 (RDP): Remote Desktop Protocol is a frequent target for attacks (e.g., brute force, exploits like BlueKeep). If improperly configured or unpatched, it poses a significant risk, especially on externally facing systems.
Port 21 (FTP): While FTP can be insecure (plaintext credentials), it’s less critical than Telnet and RDP unless explicitly misconfigured.
Port 22 (SSH): SSH is generally secure when properly configured, so it’s lower priority unless vulnerabilities are detected.
Port 636 (LDAPS): This is the secure version of LDAP (using SSL/TLS), making it less concerning unless misconfigure.
Port 1723 (PPTP): PPTP is outdated and has known vulnerabilities, but it’s less commonly targeted than Telnet or RDP in modern environments.
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ Study Guide (CS0-003), Chapter 3: Vulnerability Management
NIST SP 800-41: Guidelines on Firewalls and Firewall Policy (identifying insecure services)
OWASP: Unsecure Communication (Telnet risks)
A laptop that is company owned and managed is suspected to have malware. The company implemented centralized security logging. Which of the following log sources will confirm the malware infection?
A. XDR logs
B. Firewall logs
C. IDS logs
D. MFA logs
Explanation:
XDR (Extended Detection and Response) logs are the best source to confirm a malware infection on a company-owned laptop. XDR provides comprehensive endpoint monitoring, including behavioral analysis, file integrity checks, and threat detection, which can identify malware indicators like suspicious processes or network activity. Firewall logs track network traffic but may not confirm endpoint malware. IDS logs detect network-based intrusions but lack endpoint context. MFA logs record authentication events, not malware activity.
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ Study Guide (CS0-003), Chapter 2: Security Operations
NIST SP 800-83: Guide to Malware Incident Prevention and Handling
CySA+ Objective: 2.1 – Analyze logs to confirm indicators of compromise
3.5s
How can Grok help?
The SOC received a threat intelligence notification indicating that an employee's credentials were found on the dark web. The user's web and log-in activities were reviewed for malicious or anomalous connections, data uploads/downloads, and exploits. A review of the controls confirmed multifactor authentication was enabled. Which of the following should be done first to mitigate impact to the business networks and assets?
A. Perform a forced password reset.
B. Communicate the compromised credentials to the user.
C. Perform an ad hoc AV scan on the user's laptop.
D. Review and ensure privileges assigned to the user's account reflect least privilege.
E. Lower the thresholds for SOC alerting of suspected malicious activity.
Explanation:
Since the employee’s credentials were found on the dark web, the immediate priority is to perform a forced password reset to prevent unauthorized access to business networks and assets. Even with multifactor authentication (MFA) enabled, compromised credentials pose a risk if MFA is bypassed or not applied universally. This action directly mitigates the threat of attackers using the credentials. Communicating to the user is important but secondary to securing the account. An ad hoc AV scan addresses potential malware, not credential misuse. Reviewing privileges is a good practice but less urgent than neutralizing the compromised credentials. Lowering SOC alert thresholds enhances monitoring but doesn’t directly address the immediate threat.
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ Study Guide (CS0-003), Chapter 4: Incident Response
NIST SP 800-61 Rev. 2: Computer Security Incident Handling Guide (credential compromise response).
A company has the following security requirements:
. No public IPs
· All data secured at rest
. No insecure ports/protocols
After a cloud scan is completed, a security analyst receives reports that several misconfigurations are putting the company at risk. Given the following cloud scanner output:
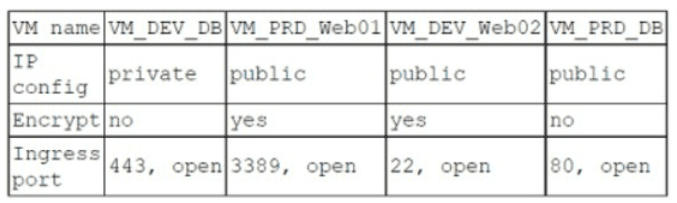
Which of the following should the analyst recommend be updated first to meet the security
requirements and reduce risks?
A. VM_PRD_DB
B. VM_DEV_DB
C. VM_DEV_Web02
D. VM_PRD_Web01
Explanation:
The company’s security requirements include no public IPs, all data secured at rest, and no insecure ports/protocols. VM_PRD_DB (a production database) should be prioritized for updates because misconfigurations in a production database are likely to involve critical issues, such as exposed public IPs, unencrypted data at rest, or insecure ports (e.g., unencrypted database protocols like MySQL on port 3306 or PostgreSQL on 5432). These pose a high risk to sensitive data in a production environment. VM_DEV_DB (development database) is lower priority due to its non-production status. VM_PRD_Web01 and VM_DEV_Web02 (web servers) may have issues, but databases typically store sensitive data, making VM_PRD_DB the most critical to address first.
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ Study Guide (CS0-003), Chapter 3: Vulnerability Management
NIST SP 800-53: SC-28 (Protection of Data at Rest), AC-3 (Access Control)
OWASP Cloud Security: Misconfiguration Risks.
An analyst is evaluating the following vulnerability report:
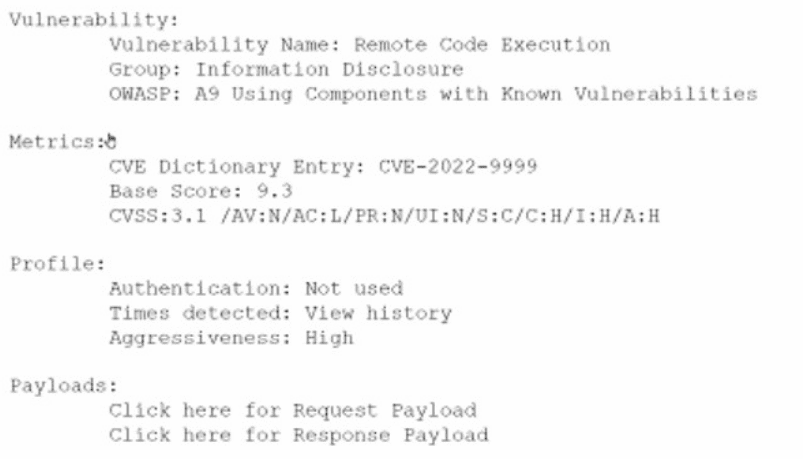
Which of the following vulnerability report sections provides information about the level of
impact on data confidentiality if a successful exploitation occurs?
A. Payloads
B. Metrics
C. Vulnerability
D. Profile
Explanation:
In a vulnerability report, the Metrics section typically includes the CVSS (Common Vulnerability Scoring System) score, which quantifies the impact of a vulnerability on confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Specifically, the CVSS Confidentiality Impact (C) metric (e.g., C:H for High) indicates the level of impact on data confidentiality if the vulnerability is exploited. The Payloads section describes exploit code or methods, not impact. The Vulnerability section details the flaw itself. The Profile section may describe the system or environment, not the specific impact on confidentiality.
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ Study Guide (CS0-003), Chapter 3: Vulnerability Management
A penetration tester submitted data to a form in a web application, which enabled the penetration tester to retrieve user credentials. Which of the following should be recommended for remediation of this application vulnerability?
A. Implementing multifactor authentication on the server OS
B. Hashing user passwords on the web application
C. Performing input validation before allowing submission
D. Segmenting the network between the users and the web server
Explanation:
The vulnerability described suggests an input validation flaw, such as SQL injection or cross-site scripting (XSS), allowing the penetration tester to retrieve user credentials by submitting malicious data to a web form. Performing input validation (e.g., sanitizing and validating user inputs) prevents malicious data from being processed, directly addressing the root cause. Implementing multifactor authentication (MFA) on the server OS enhances authentication security but doesn’t fix the application’s input flaw. Hashing user passwords protects stored credentials but doesn’t prevent the exploit if credentials are extracted via the form. Segmenting the network improves security but doesn’t address the application vulnerability itself.
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ Study Guide (CS0-003), Chapter 3: Vulnerability Management
OWASP Top Ten (2021): A03 – Injection (emphasizes input validation)
NIST SP 800-53: SI-10 (Input Validation)
Which of the following best describes the goal of a disaster recovery exercise as preparation for possible incidents?
A. TO provide metrics and test continuity controls
B. To verify the roles of the incident response team
C. To provide recommendations for handling vulnerabilities
D. To perform tests against implemented security controls
Explanation:
A disaster recovery (DR) exercise is primarily conducted to:
Test business continuity and recovery controls (e.g., backups, failovers, DR sites)
Measure recovery time objectives (RTO) and recovery point objectives (RPO)
Ensure systems can be restored within acceptable timeframes
This aligns directly with:
➡"To provide metrics and test continuity controls"
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ CS0-003 Exam Objectives (Domain 3.5):
"Given a scenario, apply common prevention, detection, and recovery controls for organizational security."
Let me know if you want a cheat sheet for DR testing types.
A company is implementing a vulnerability management program and moving from an onpremises environment to a hybrid IaaS cloud environment. Which of the following implications should be considered on the new hybrid environment?
A. The current scanners should be migrated to the cloud
B. Cloud-specific misconfigurations may not be detected by the current scanners
C. Existing vulnerability scanners cannot scan laaS systems
D. Vulnerability scans on cloud environments should be performed from the cloud
Explanation:
When moving to a hybrid IaaS cloud environment, it's crucial to understand that:
Traditional on-premises vulnerability scanners often do not detect cloud-specific risks, such as:
IAM misconfigurations
Insecure storage buckets
Excessive permissions
Publicly exposed services
These cloud misconfigurations are different from typical OS/app-level vulnerabilities.
Why the other options are incorrect:
The current scanners should be migrated to the cloud"
➤ Not necessarily; scanners can run on-prem and still reach cloud assets (depending on routing/security).
"Existing vulnerability scanners cannot scan IaaS systems"
➤ Not true. Most enterprise scanners can scan IaaS, but may miss configuration issues unless integrated with cloud-native APIs.
"Vulnerability scans on cloud environments should be performed from the cloud"
➤ It's ideal but not mandatory; scanning location depends on access, latency, and security design.
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ CS0-003 Objective 3.3 – "Assess security implications of embedded and cloud-integrated systems."
A security analyst has found the following suspicious DNS traffic while analyzing a packet
capture:
• DNS traffic while a tunneling session is active.
• The mean time between queries is less than one second.
• The average query length exceeds 100 characters.
Which of the following attacks most likely occurred?
A. DNS exfiltration
B. DNS spoofing
C. DNS zone transfer
D. DNS poisoning
Explanation:
The key indicators mentioned in the packet capture point to DNS exfiltration, which is a form of data exfiltration using DNS queries. Here's why:
DNS traffic during a tunneling session → Suggests covert channels are in use.
Mean time between queries < 1 second → Indicates automated, high-frequency requests (unusual for normal DNS usage).
Average query length > 100 characters → Implies payloads or encoded data are being transmitted within DNS requests.
DNS exfiltration typically uses encoded or encrypted data inside DNS queries to bypass security controls and send data outside the network.
Why the other options are incorrect:
DNS spoofing: Involves forging DNS responses to redirect traffic—not related to the pattern of traffic shown.
DNS zone transfer: Attempts to pull an entire DNS zone file from a server; it’s a one-time large request, not many small ones.
DNS poisoning: Involves injecting false entries into a DNS cache—again, unrelated to query frequency or length.
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ CS0-003 Exam Objective 2.2 – "Analyze potential indicators to determine the type of attack."
Let me know if you'd like a diagram of how DNS exfiltration works.
| Page 8 out of 45 Pages |
