A company receives a penetration test report summary from a third party. The report summary indicates a proxy has some patches that need to be applied. The proxy is sitting in a rack and is not being used, as the company has replaced it with a new one. The CVE score of the vulnerability on the proxy is a 9.8. Which of the following best practices should the company follow with this proxy?
A. Leave the proxy as is.
B. Decomission the proxy.
C. Migrate the proxy to the cloud.
D. Patch the proxy
Explanation:
Even though the proxy has a critical CVE score of 9.8, it is no longer in use. Leaving unused, unpatched hardware on the network poses a serious security risk, as attackers could exploit it even if it's not actively used.
Best practice in this case is to:
Remove or decommission unused assets.
Avoid wasting time or resources patching unused systems.
Reduce the organization’s attack surface.
Reference:
NIST SP 800-128: Guide for Security-Focused Configuration Management of Information Systems — “Decommission unused systems to reduce attack surfaces.”
CIS Controls v8 – Control 1: Inventory and Control of Enterprise Assets.
A systems administrator notices unfamiliar directory names on a production server. The administrator reviews the directory listings and files, and then concludes the server has been compromised. Which of the following steps should the administrator take next?
A. Inform the internal incident response team.
B. Follow the company's incident response plan.
C. Review the lessons learned for the best approach
D. Determine when the access started
Explanation:
The question asks for the next step a systems administrator should take after concluding a production server has been compromised due to unfamiliar directory names. Following the company's incident response plan is the most appropriate next step, as it provides a structured, organization-specific process to handle the incident effectively, ensuring containment, evidence preservation, and proper escalation. This aligns with the CS0-003 exam’s Incident Response and Management (Domain 3) and Security Operations (Domain 1) objectives, which emphasize adhering to formal incident response procedures.
Why B is Correct:
Incident Response Plan Overview: The incident response plan (e.g., based on NIST SP 800-61) outlines steps for handling security incidents, including containment, eradication, recovery, and communication. It ensures a consistent, compliant response tailored to the organization’s needs.
Next Step After Conclusion: Once the administrator confirms a compromise (based on unfamiliar directories), the plan guides immediate actions, such as isolating the server, preserving evidence (e.g., logs, memory dumps), and notifying the incident response team. Following the plan ensures no critical steps are missed.
Healthcare Context: In a healthcare organization (per prior questions), the plan likely includes HIPAA-compliant procedures to protect PHI, such as isolating compromised systems to prevent data exfiltration and documenting actions for regulatory reporting.
CS0-003 Alignment: Domain 3 emphasizes executing incident response plans to manage compromises, while Domain 1 supports following organizational procedures to maintain security operations.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Inform the internal incident response team
Reason: Informing the incident response team is a critical step but is typically part of the incident response plan. The plan specifies when and how to notify the team (e.g., via ticketing system, phone call), ensuring proper escalation and documentation. Following the plan first ensures all necessary actions (e.g., containment) are taken before or alongside notification, making it the broader, correct step.
C. Review the lessons learned for the best approach
Reason: Reviewing lessons learned occurs in the Lessons Learned phase (post-incident) to improve future responses, not during an active compromise. The administrator needs to act immediately to contain and mitigate the incident, not reflect on past incidents, making this step irrelevant at this stage.
D. Determine when the access started
Reason: Determining when the access started (e.g., via log analysis) is part of the Identification or Analysis phase, but it follows initial containment to prevent further damage. The incident response plan would guide containment (e.g., isolating the server) before diving into forensic analysis, as premature investigation risks altering evidence or allowing the attacker to escalate.
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ (CS0-003) Exam Objectives, Domains 1 (Security Operations) and 3 (Incident Response and Management), www.comptia.org, covering incident response procedures.
CompTIA CySA+ Study Guide: Exam CS0-003 by Chapple and Seidl, discussing incident response plans and initial response steps.
During a scan of a web server in the perimeter network, a vulnerability was identified that could be exploited over port 3389. The web server is protected by a WAF. Which of the following best represents the change to overall risk associated with this vulnerability?
A. The risk would not change because network firewalls are in use.
B. The risk would decrease because RDP is blocked by the firewall.
C. The risk would decrease because a web application firewall is in place.
D. The risk would increase because the host is external facing.
Explanation:
Port 3389 is used for Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) — a common target for attackers, especially on external-facing servers. The fact that this is a web server in the perimeter network (DMZ) and accessible from the internet increases the exposure and likelihood of attack.
Even though a Web Application Firewall (WAF) is in place, a WAF only protects HTTP/HTTPS traffic, not RDP. Therefore, the presence of the WAF does not mitigate the RDP vulnerability.
Why the other options are incorrect:
"The risk would not change because network firewalls are in use"
→ Incorrect. Just having a firewall doesn't guarantee protection — if port 3389 is open, the vulnerability is still accessible.
"The risk would decrease because RDP is blocked by the firewall"
→ That would only be true if RDP is actually blocked — but the scenario says a vulnerability is present over port 3389, implying it's open.
"The risk would decrease because a web application firewall is in place"
→ False. WAFs only protect against web application threats, not remote desktop exploits.
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ CS0-003 Exam Objective 2.1 – Given a scenario, apply security concepts in support of organizational risk mitigation.
NIST SP 800-30 (Risk Assessment): Exposure and asset value increases risk.
A zero-day command injection vulnerability was published. A security administrator is
analyzing the following logs for evidence of adversaries attempting to exploit the
vulnerability:

Which of the following log entries provides evidence of the attempted exploit?
A. Log entry 1
B. Log entry 2
C. Log entry 3
D. Log entry 4
Explanation:
A zero-day command injection vulnerability allows attackers to execute arbitrary system commands by injecting them into input fields (e.g., via web forms or APIs). To identify an exploit attempt, the security administrator should look for log entries showing suspicious commands, such as shell commands, file manipulation, or system reconnaissance attempts (e.g., cat /etc/passwd, curl, wget). Without specific log details for entries 1–4, the correct choice is the entry displaying such malicious patterns, indicating an attempt to exploit the vulnerability.
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ Study Guide (CS0-003), Chapter 4: Incident Response
OWASP Top Ten (2021): A03 – Injection
NIST SP 800-61 Rev. 2: Computer Security Incident Handling Guide (log analysis)
CySA+ Objective: 2.1 – Analyze logs to identify indicators of compromise
A recent penetration test discovered that several employees were enticed to assist attackers by visiting specific websites and running downloaded files when prompted by phone calls. Which of the following would best address this issue?
A. Increasing training and awareness for all staff
B. Ensuring that malicious websites cannot be visited
C. Blocking all scripts downloaded from the internet
D. Disabling all staff members' ability to run downloaded applications
Explanation:
The issue describes a social engineering attack (e.g., phishing combined with vishing), where employees were tricked into visiting malicious websites and running downloaded files. Increasing training and awareness educates staff to recognize and avoid such tactics, addressing the root cause—human error. Blocking malicious websites is helpful but insufficient, as attackers can use new or unknown sites. Blocking all scripts may disrupt legitimate operations and not prevent all malicious files. Disabling the ability to run downloaded applications is overly restrictive and impractical for most workflows
.
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ Study Guide (CS0-003), Chapter 2: Security Operations
NIST SP 800-53: AT-2 (Security Awareness Training)
During security scanning, a security analyst regularly finds the same vulnerabilities in a critical application. Which of the following recommendations would best mitigate this problem if applied along the SDLC phase?
A. Conduct regular red team exercises over the application in production
B. Ensure that all implemented coding libraries are regularly checked
C. Use application security scanning as part of the pipeline for the CI/CDflow
D. Implement proper input validation for any data entry form
Explanation:
Regularly finding the same vulnerabilities in a critical application indicates a lack of early detection and remediation in the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). Integrating application security scanning into the CI/CD pipeline (e.g., Static Application Security Testing (SAST) or Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST)) ensures vulnerabilities are identified and fixed during development, before deployment. This proactive approach reduces recurring issues. Red team exercises test production environments but don’t address development flaws. Checking coding libraries helps but is too narrow. Input validation mitigates specific vulnerabilities (e.g., injection) but isn’t comprehensive for all recurring issues.
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ Study Guide (CS0-003), Chapter 3: Vulnerability Management
OWASP Secure Coding Practices: https://owasp.org/www-project-secure-coding-practices-quick-reference-guide/
NIST SP 800-53: SA-11 (Developer Security Testing and Evaluation)
Due to reports of unauthorized activity that was occurring on the internal network, an
analyst is performing a network discovery. The analyst runs an Nmap scan against a
corporate network to evaluate which devices were operating in the environment. Given the
following output:
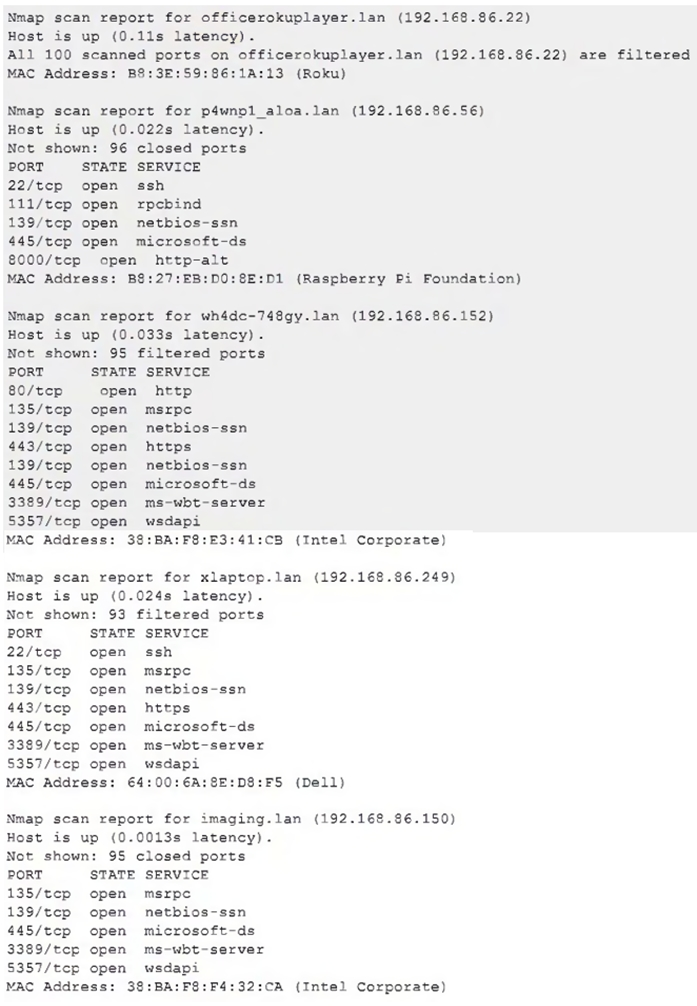
Which of the following choices should the analyst look at first?
A. wh4dc-748gy.lan (192.168.86.152)
B. lan (192.168.86.22)
C. imaging.lan (192.168.86.150)
D. xlaptop.lan (192.168.86.249)
E. p4wnp1_aloa.lan (192.168.86.56)
Explanation:
The device named p4wnp1_aloa.lan stands out as suspicious and should be investigated first. The name resembles P4wnP1 ALOHA, a known open-source tool used for penetration testing and malicious activities, often deployed as a rogue device or USB attack platform. Its presence on a corporate network, especially amid reports of unauthorized activity, suggests it could be an attacker’s device or compromised system. The other devices (wh4dc-748gy.lan, lan, imaging.lan, xlaptop.lan) have names typical of corporate assets (e.g., workstations, servers, or imaging systems) and are less likely to be the immediate source of unauthorized activity without further evidence.
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ Study Guide (CS0-003), Chapter 2: Security Operations (Network Discovery and Threat Identification)
NIST SP 800-61 Rev. 2: Computer Security Incident Handling Guide (Identifying Rogue Devices)
P4wnP1 ALOHA Documentation: https://github.com/RoganDawes/P4wnP1_aloa (describes its use in penetration testing)
Results of a SOC customer service evaluation indicate high levels of dissatisfaction with the inconsistent services provided after regular work hours. To address this, the SOC lead drafts a document establishing customer expectations regarding the SOC's performance and quality of services. Which of the following documents most likely fits this description?
A. Risk management plan
B. Vendor agreement
C. Incident response plan
D. Service-level agreement
Explanation:
An SLA defines customer expectations for performance and quality of services, including availability, response times, and support consistency, especially for after-hours services. It directly addresses the SOC’s service delivery issues. A risk management plan focuses on identifying and mitigating risks, not service quality. A vendor agreement outlines terms with third-party providers, not SOC performance. An incident response plan details steps for handling security incidents, not customer service expectations.
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ Study Guide (CS0-003), Chapter 5: Reporting and Communication
NIST SP 800-53: SA-9 (External System Services, covering SLAs)
A technician identifies a vulnerability on a server and applies a software patch. Which of the following should be the next step in the remediation process?
A. Testing
B. Implementation
C. Validation
D. Rollback
Explanation:
After applying a software patch to address a vulnerability, the next step in the remediation process is validation. This involves verifying that the patch successfully mitigated the vulnerability (e.g., by rescanning the server) and ensuring the system functions correctly without introducing new issues. Testing occurs before patching in a controlled environment. Implementation refers to applying the patch, which has already been done. Rollback is only needed if validation fails.
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ Study Guide (CS0-003), Chapter 3: Vulnerability Management
NIST SP 800-40 Rev. 4: Guide to Enterprise Patch Management Planning
An MSSP received several alerts from customer 1, which caused a missed incident response deadline for customer 2. Which of the following best describes the document that was violated?
A. KPI
B. SLO
C. SLA
D. MOU
Explanation:
An SLA defines specific performance commitments, such as incident response deadlines, between a Managed Security Service Provider (MSSP) and its customers. Missing a deadline for Customer 2 due to prioritizing Customer 1’s alerts indicates a violation of the SLA with Customer 2. KPI (Key Performance Indicator) measures performance but isn’t a binding agreement. SLO (Service-level Objective) is a goal within an SLA, not the document itself. MOU (Memorandum of Understanding) outlines mutual agreements but lacks the enforceable specifics of an SLA.
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ Study Guide (CS0-003), Chapter 5: Reporting and Communication
NIST SP 800-53: SA-9 (External System Services, covering SLAs)
| Page 7 out of 45 Pages |
