A Linux administrator is troubleshooting a memory-related issue. Based on the output of the commands:

Which of the following commands would address the issue?
A.
top -p 8321
B.
kill -9 8321
C.
renice -10 8321
D.
free 8321
kill -9 8321
Summary:
The administrator is troubleshooting a memory-related issue. The ps aux output shows that process ID (PID) 8321, named bad_process, is consuming 80% of the system's memory (%MEM 80.0). This level of memory usage is extreme and is very likely the direct cause of the performance issue, potentially leading to system instability or unresponsiveness due to memory exhaustion and swapping.
Correct Option:
B. kill -9 8321:
This command will forcefully terminate the problematic process. The -9 signal (SIGKILL) cannot be caught or ignored by the process and will immediately stop it, freeing up the massive amount of memory it was consuming. This is the most direct and effective action to resolve a memory issue caused by a single runaway process.
Incorrect Options:
A. top -p 8321:
This command would only monitor the specific process 8321 within the top interface. It is a diagnostic command for observing resource usage in real-time but takes no corrective action to stop the process or free up memory.
C. renice -10 8321:
The renice command changes the scheduling priority (niceness) of a process. A value of -10 would give the process a higher priority, causing the CPU scheduler to favor it. This would not reduce its memory consumption and could make the overall system performance worse by allocating more CPU time to the problematic process.
D. free 8321:
The free command displays overall memory usage for the system (total, used, free, etc.) and does not accept a PID as an argument. This command is invalid and would result in an error.
Reference:
Linux man-pages project (kill): The official documentation explains the kill command and the SIGKILL signal (9).
A Linux administrator is reviewing changes to a configuration file that includes the following section:
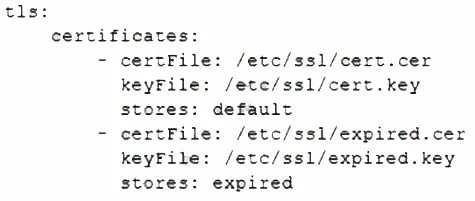
The Linux administrator is trying to select the appropriate syntax formatter to correct any issues with the configuration file. Which of the following should the syntax formatter support to meet this goal?
A.
Markdown
B.
XML
C.
YAML
D.
JSON
YAML
Summary:
The provided configuration file section uses a structure of key-value pairs, colons for assignment, and hyphens to denote list items under a parent key. This syntax, featuring indentation for nesting and the lack of brackets or commas, is characteristic of a specific data serialization language designed to be human-readable and easy to write.
Correct Option:
C. YAML:
The syntax formatter must support YAML (YAML Ain't Markup Language). The displayed configuration is a classic example of YAML syntax. Key indicators are:
Key-value pairs using a colon and a space (name: httpd).
A sequence (list) denoted by hyphens (- httpd, - mariadb-server).
Reliance on indentation for structure rather than explicit brackets or braces.
Incorrect Options:
A. Markdown:
Markdown is a lightweight markup language used for formatting plain text, commonly seen in README files. It uses symbols like # for headers, * for bold/italic, and - for lists, but it does not use colons for key-value pairs or have a formal structure for nested configuration data like the example.
B. XML:
XML (eXtensible Markup Language) uses tags enclosed in angle brackets (e.g.,
D. JSON:
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) uses curly braces {} to define objects and square brackets [] for arrays. It requires double quotes around keys and string values, and uses commas to separate elements. The given configuration does not use any of these structural characters.
Reference:
Official CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Exam Objectives: This question aligns with the general knowledge required across several objectives, particularly those involving automation and configuration management (Objective 4.1). YAML is the de-facto standard for configuration files in many modern DevOps tools like Ansible, Kubernetes, and Docker Compose. The official YAML website (yaml.org) is the primary specification.
A cloud engineer needs to launch a container named web-01 in background mode. Which of the following commands will accomplish this task''
A.
docker builder -f —name web-01 httpd
B.
docker load --name web-01 httpd
C.
docker ps -a --name web-01 httpd
D.
docker run -d --name web-01 httpd
docker run -d --name web-01 httpd
Summary:
The task is to launch a new container from an image, assign it a specific name, and run it in the background (detached mode). The correct command must be one that creates and starts a new container, includes the flags to name it and run it detached, and specifies the source image.
Correct Option:
D. docker run -d --name web-01 httpd:
This is the correct command.
docker run is the command used to create and start a new container from an image.
The -d flag runs the container in detached mode (in the background).
The --name web-01 flag assigns the specified name to the new container.
httpd is the image name used to create the container.
Incorrect Options:
A. docker builder -f --name web-01 httpd:
This command is invalid. docker builder is not a standard command. The command to build an image from a Dockerfile is docker build.
B. docker load --name web-01 httpd:
The docker load command is used to load an image into the local Docker repository from a tar archive. It does not create or run a container, and it does not accept the --name flag.
docker load loads an image from a file, it does not pull from a registry or run a container.
C. docker ps -a --name web-01 httpd:
The docker ps command is used to list existing containers. It is a query command, not one used to launch a new container. It does not accept an image name (httpd) as an argument.
Reference:
Official CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Exam Objectives: This scenario falls under Objective 1.5: "Given a scenario, manage and configure containers," which includes using Docker commands to run and manage containers. Knowing the docker run command with flags like -d and --name is fundamental.
A Linux engineer needs to create a custom script, cleanup.sh, to run at boot as part of the system services. Which of the following processes would accomplish this task?
A.
Create a unit file in the /etc/default/ directory.
systemctl enable cleanup
systemctl is-enabled cleanup
B.
Create a unit file in the /etc/ske1/ directory.
systemctl enable cleanup
systemctl is-enabled cleanup
C.
Create a unit file in the /etc/systemd/system/ directory.
systemctl enable cleanup
systemctl is-enabled cleanup
D.
Create a unit file in the /etc/sysctl.d/ directory.
systemctl enable cleanup
systemctl is-enabled cleanup
Create a unit file in the /etc/systemd/system/ directory.
systemctl enable cleanup
systemctl is-enabled cleanup
Summary:
To run a custom script as a system service at boot time on a modern Linux system using systemd, the administrator must create a unit file. This unit file defines the service, including its description, when it should start, and the command to execute. The unit file must be placed in the correct directory so the systemd process can find and manage it.
Correct Option:
C. Create a unit file in the /etc/systemd/system/ directory. systemct1 enable cleanup systemct1 is-enabled cleanup: This is the correct process.
The /etc/systemd/system/ directory is the standard location for administrator-created and third-party unit files.
Creating a file here (e.g., cleanup.service) allows systemd to manage the script as a service.
The systemctl enable command creates the necessary symlinks to start the service at boot.
The systemctl is-enabled command verifies that the service has been successfully enabled to start at boot.
Incorrect Options:
A. /etc/default/:
This directory is used for storing environment variables and default configuration settings for some services and scripts (like those in /etc/init.d/). It is not the location for systemd unit files.
B. /etc/ske1/:
This is a misspelling and not a standard directory in a Linux filesystem hierarchy. The correct directory for skeleton files (default user profile files) is /etc/skel/, which is unrelated to system services.
D. /etc/sysctl.d/:
This directory is used for kernel parameter configuration files. Settings placed here (e.g., 90-custom.conf) are loaded at boot to modify kernel parameters using the sysctl command. It is not used for defining system services or scripts.
Reference:
Official CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Exam Objectives: This scenario directly tests Objective 3.1: "Given a scenario, use the appropriate system and service management commands to accomplish administrative tasks," which includes creating and managing systemd services. Knowing the correct location for custom unit files (/etc/systemd/system/) and the commands to enable them is a core requirement.
A Linux system fails to start and delivers the following error message:

Which of the following commands can be used to address this issue?
A.
fsck.ext4 /dev/sda1
B.
partprobe /dev/sda1
C.
fdisk /dev/sda1
D.
mkfs.ext4 /dev/sda1
fsck.ext4 /dev/sda1
Summary:
The boot process is failing because the filesystem on /dev/sda1 has errors and is being mounted as read-only to prevent further damage. The kernel has detected an unclean filesystem journal, which indicates the filesystem was not unmounted properly (e.g., due to a power loss or system crash). The system cannot proceed until this filesystem inconsistency is repaired.
Correct Option:
A. fsck.ext4 /dev/sda1:
This is the correct command. fsck (filesystem check) is the utility used to check and repair inconsistencies in a Linux filesystem. Since the error specifies the filesystem is ext4, using fsck.ext4 directly is appropriate. The administrator would likely need to run this from a rescue environment since the root filesystem is affected.
Incorrect Options:
B. partprobe /dev/sda1:
This command informs the operating system kernel of partition table changes. It is used after modifying a partition table with a tool like fdisk and has no ability to repair filesystem errors.
C. fdisk /dev/sda1:
This is a disk partitioning tool. It is used to create, delete, or modify partitions, not to repair the filesystem on a partition. Using this would risk destroying data.
D. mkfs.ext4 /dev/sda1:
This command creates a new ext4 filesystem on the partition. It is a formatting command that would completely erase all existing data on /dev/sda1, which is a destructive action and not a repair.
Reference:
Linux man-pages project (fsck): The official documentation describes the purpose of fsck for checking and repairing filesystems.
A Linux administrator needs to redirect all HTTP traffic temporarily to the new proxy server 192.0.2.25 on port 3128. Which of the following commands will accomplish this task?
A. iptables -t nat -D PREROUTING -p tcp --sport 80 -j DNAT - -to-destination 192.0.2.25:3128
B. iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p top --dport 81 -j DNAT –-to-destination
192.0.2.25:3129
C. iptables -t nat -I PREROUTING -p top --sport 80 -j DNAT –-to-destination
192.0.2.25:3129
D. iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 80 -j DNAT –-to-destination 192.0.2.25:3128
Summary:
The task requires redirecting HTTP traffic, which uses TCP port 80, to a new proxy server at a specific IP and port. This is achieved using iptables with the nat table to modify the destination of packets before they are routed. The rule must match outgoing HTTP traffic and change its destination to the proxy server.
Correct Option:
D. iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 80 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.0.2.25:3128: This command is correctly structured.
-t nat uses the NAT table for destination translation.
-A PREROUTING appends the rule to the PREROUTING chain, where DNAT is performed before the routing decision.
-p tcp --dport 80 matches TCP packets destined for port 80 (HTTP).
-j DNAT --to-destination 192.0.2.25:3128 jumps to the DNAT target, redirecting packets to the proxy server on port 3128.
Incorrect Options:
A. iptables -t nat -D PREROUTING ...:
The -D flag is used to delete a rule from a chain, not to add one. Furthermore, --sport 80 matches the source port 80, which is incorrect; we want to match the destination port.
B. iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p top --dport 81 ...:
This command has two critical errors. First, the protocol is misspelled as top instead of tcp. Second, it matches port 81 instead of the standard HTTP port 80. The proxy port is also incorrect (3129 instead of 3128).
C. iptables -t nat -I PREROUTING -p top --sport 80 ...:
This command also uses the misspelled protocol top. It uses -I to insert the rule, which would work, but it incorrectly matches the source port (--sport 80) instead of the destination port. The proxy port is also incorrect.
Reference:
Netfilter/iptables Project Documentation: The official documentation details the syntax for the nat table and the DNAT target.
A DevOps engineer needs to allow incoming traffic to ports in the range of 4000 to 5000 on a Linux server. Which of the following commands will enforce this rule?
A.
iptables -f filter -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 4000:5000 -A ACCEPT
B.
iptables -t filter -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 4000:5000 -j ACCEPT
C.
iptables filter -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 4000:5000 -D ACCEPT
D.
iptables filter -S INPUT -p tcp --dport 4000:5000 -A ACCEPT
iptables -t filter -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 4000:5000 -j ACCEPT
Summary:
The engineer needs to create a firewall rule that accepts incoming TCP traffic on a range of ports (4000 to 5000). The iptables command is used to configure the Linux kernel's netfilter firewall. The correct command must use the proper syntax to append a rule to the INPUT chain of the filter table, matching the TCP protocol and the specified destination port range, and then jump to the ACCEPT target.
Correct Option:
B. iptables -t filter -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 4000:5000 -j ACCEPT:
This command is correctly structured.
-t filter specifies the table (filter is the default table, so this is often omitted, but it is correct to include it).
-A INPUT appends the rule to the INPUT chain.
-p tcp specifies the TCP protocol.
--dport 4000:5000 defines the destination port range.
-j ACCEPT is the target action, meaning to accept the packet.
Incorrect Options:
A. iptables -f filter -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 4000:5000 -A ACCEPT:
This command uses -f (which is not a standard flag for specifying a table; the correct flag is -t) and -I (which inserts a rule at the beginning of the chain). It also incorrectly uses -A ACCEPT instead of -j ACCEPT.
C. iptables filter -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 4000:5000 -D ACCEPT:
This command omits the -t flag for the table. It also uses -D ACCEPT, where -D is the command to delete a rule, not to set a jump target.
D. iptables filter -S INPUT -p tcp --dport 4000:5000 -A ACCEPT:
This command omits the -t flag and uses -S (which is for displaying the rules of a specific chain) and then tries to combine it with rule-adding parameters, which is invalid syntax.
Reference:
Netfilter/iptables Project Documentation: The official documentation details the correct syntax for the iptables command.
When trying to log in remotely to a server, a user receives the following message:
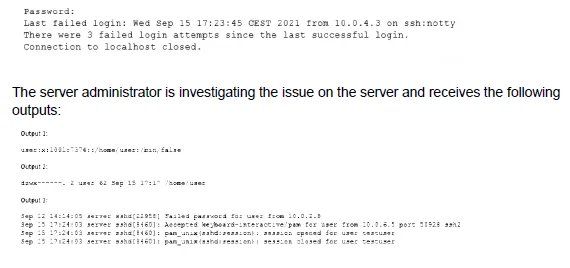
Which of the following is causing the issue?
A.
The wrong permissions are on the user’s home directory.
B.
The account was locked out due to three failed logins.
C.
The user entered the wrong password.
D.
The user has the wrong shell assigned to the account.
The user has the wrong shell assigned to the account.
Summary:
The user receives a "Connection closed" message immediately after the last failed login attempt, without being prompted for a password again. The key evidence is in Output 1 from /etc/passwd, which shows the user's login shell is set to /bin/false. This shell is not a functional interactive shell; it simply returns a false status and exits immediately. When SSH successfully authenticates a user, it launches their assigned shell. If that shell is /bin/false, it exits instantly, closing the connection.
Correct Option:
D. The user has the wrong shell assigned to the account:
This is the direct cause. The user's shell in /etc/passwd is /bin/false, which is often used to disable logins for service accounts. When SSH authenticates the user, it launches /bin/false, which exits immediately, resulting in the closed connection. This happens after authentication, which is why the log shows an "Accepted" message before the session closes.
Incorrect Options:
A. The wrong permissions on the user’s home directory:
Output 2 shows the home directory permissions are 700 (drwx------), which is correct and secure for a user's home directory. This is not the cause.
B. The account was locked out due to three failed logins:
Account lockouts typically result in a specific "Account locked" or "Permission denied" message, not a closed connection after an accepted login. The log (Output 3) shows a successful "Accepted" authentication followed by a session open/close, which indicates the login was technically successful but the session couldn't be maintained.
C. The user entered the wrong password:
The log in Output 3 shows a final "Accepted" message for the user, confirming the correct password was entered for that specific session. The previous failures were from a different IP and are not the reason for the immediate disconnect after the successful login.
Reference:
Linux man-pages project (passwd): The /etc/passwd file format defines the user's login shell in the last field. A non-existent or non-functional shell will prevent successful login.
Which of the following enables administrators to configure and enforce MFA on a Linux system?
A.
Kerberos
B.
SELinux
C.
PAM
D.
PKI
PAM
Summary:
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) requires integrating different authentication methods (like passwords, one-time codes, or biometrics) into the system's login process. This integration happens at the authentication layer, which is modular and configurable in Linux. The correct framework allows administrators to define a stack of authentication modules that must be satisfied for a successful login.
Correct Option:
C. PAM:
This is the correct framework. Pluggable Authentication Modules (PAM) is the subsystem in Linux that handles authentication tasks for applications and services. Administrators can configure MFA by editing PAM configuration files (in /etc/pam.d/) to require multiple authentication methods. For example, a configuration can first require a password (pam_unix.so) and then require a one-time token from a Google Authenticator module (pam_google_authenticator.so).
Incorrect Options:
A. Kerberos:
Kerberos is a network authentication protocol that uses tickets to allow nodes to communicate over a non-secure network to prove their identity to one another. It is a single sign-on (SSO) system, not a framework for configuring multiple distinct factors at the OS login prompt.
B. SELinux:
Security-Enhanced Linux is a kernel security module that provides a mechanism for supporting access control security policies, including mandatory access controls (MAC). It focuses on restricting what programs and users can do after they are logged in (file access, network ports, etc.), not on how they authenticate during the login process.
D. PKI:
A Public Key Infrastructure is a set of roles, policies, hardware, software, and procedures needed to create, manage, distribute, use, store, and revoke digital certificates and manage public-key encryption. It is used for asymmetric cryptography and can be one factor in an MFA setup (e.g., using a smart card), but PKI itself is not the system that enforces the multi-factor policy; that is the role of PAM.
Reference:
Official CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Exam Objectives: This knowledge aligns with Objective 4.2: "Given a scenario, implement and configure Linux firewalls and access control options," which includes implementing and configuring access controls. PAM is the primary technology for configuring advanced authentication methods on a Linux system.
Which of the following technologies provides load balancing, encryption, and observability in containerized environments?
A.
Virtual private network
B.
Sidecar pod
C.
Overlay network
D.
Service mesh
Service mesh
Summary:
The question asks for a technology specifically designed for containerized environments that consolidates the advanced networking functions of load balancing (distributing traffic), encryption (securing communication with mTLS), and observability (providing metrics, logs, and traces). This describes a dedicated infrastructure layer that manages service-to-service communication in a microservices architecture.
Correct Option:
D. Service mesh:
This is the correct technology. A service mesh is a dedicated infrastructure layer for handling service-to-service communication in a containerized application. Its key features include:
Load Balancing:
Intelligently distributing traffic between instances of a service.
Encryption:
Automatically encrypting traffic between services using mutual TLS (mTLS).
Observability:
Providing detailed telemetry data (metrics, logs, and traces) for monitoring and troubleshooting communication patterns.
Popular examples include Istio and Linkerd.
Incorrect Options:
A. Virtual private network:
A VPN is designed to create a secure, encrypted tunnel between a client and a network, or between two networks. It is not a container-specific technology and does not provide built-in load balancing or fine-grained observability for service-to-service traffic within a cluster.
B. Sidecar pod:
A sidecar is a design pattern, not a technology itself. In Kubernetes, a sidecar is a helper container that runs alongside the main application container in a pod. While a service mesh uses a sidecar pattern (by injecting a proxy container next to each service), the sidecar itself is just one component and does not encompass the full set of features like cluster-wide load balancing and observability that define a service mesh.
C. Overlay network:
An overlay network is a virtual network built on top of another network. In container orchestration (like Kubernetes), it allows pods on different nodes to communicate. While it provides connectivity, its primary purpose is not load balancing, encryption, or observability. It is a foundational networking layer upon which technologies like a service mesh are built.
Reference:
Official CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Exam Objectives: This knowledge aligns with the container management concepts in Objective 1.5. Understanding advanced container networking concepts like service meshes is part of managing modern, cloud-native applications.
| Page 4 out of 48 Pages |
| XK0-005 Practice Test | Previous |
