A systems administrator configured firewall rules using firewalld. However, after the system is rebooted, the firewall rules are not present:
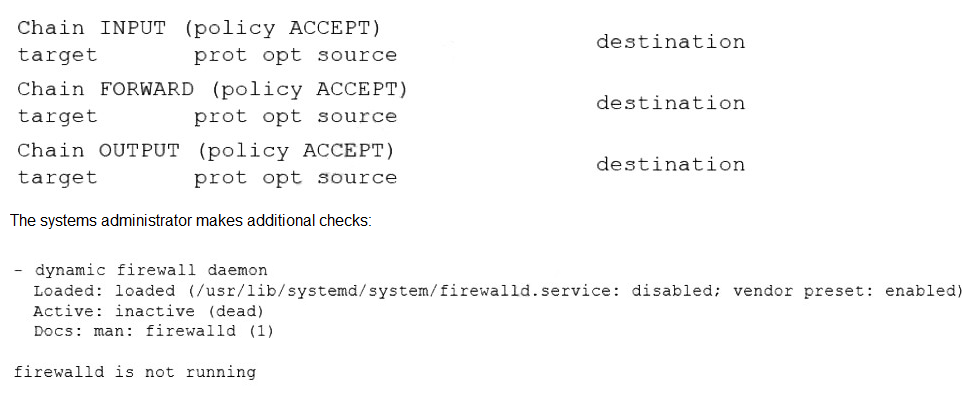
Which of the following is the reason the firewall rules are not active?
A.
iptables is conflicting with firewalld.
B.
The wrong system target is activated.
C.
FIREWALL_ARGS has no value assigned.
D.
The firewalld service is not enabled.
The firewalld service is not enabled.
Summary:
The administrator configured firewall rules with firewalld, but these rules do not persist after a reboot. The key evidence is in the systemctl status firewalld output, which shows the service is active (running) but also reveals a critical detail: the service is disabled. A disabled service is configured not to start automatically at boot, which explains why the rules are present after a manual start but disappear after a reboot.
Correct Option:
D. The firewalld service is not enabled:
This is the direct cause. The systemctl status command explicitly shows the service state as disabled. Even though the service was manually started and is currently active, the disabled state means it will not start automatically upon the next boot, causing the firewall rules to be lost.
Incorrect Options:
A. iptables is conflicting with firewalld:
The output from firewall-cmd --list-all shows the rules are active when the service is running, proving there is no conflict preventing firewalld from applying its rules. The issue is persistence across reboots, not a runtime conflict.
B. The wrong system target is activated:
The system target defines the general state of the system (like graphical or multi-user). While some services are tied to targets, firewalld is a fundamental service that should start in any multi-user target. The core issue is the service's enablement status, not the system target.
C. FIREWALL_ARGS has no value assigned:
The cat /etc/sysconfig/firewalld command shows that FIREWALL_ARGS is empty, which is actually the default and normal state. This variable is used for passing extra command-line arguments to the service and its emptiness does not prevent the service from starting or persisting rules.
Reference:
systemd Official Documentation (systemctl): The official documentation explains the difference between active (running) and enabled (configured to start at boot).
Several users reported that they were unable to write data to the /oracle1 directory. The following output has been provided:

Which of the following commands should the administrator use to diagnose the issue?
A.
df -i /oracle1
B.
fdisk -1 /dev/sdb1
C.
lsblk /dev/sdb1
D.
du -sh /oracle1
df -i /oracle1
Summary:
Users are unable to write data to the /oracle1 directory. The df -h output shows that the filesystem mounted at /oracle1 (/dev/sdb1) has only 5.0G of space used out of 497G available, so there is plenty of free disk space. When a filesystem has free space but users cannot write, a common cause is exhaustion of inodes. Inodes store metadata about files, and if all are used, no new files can be created, regardless of free space.
Correct Option:
A. df -i /oracle1:
This is the correct diagnostic command. The -i flag tells df to display inode information instead of block usage. This will show how many inodes are used and free on the filesystem. If the "IUse%" is 100%, it confirms the issue is a lack of inodes, preventing file creation.
Incorrect Options:
B. fdisk -1 /dev/sdb1:
The fdisk command is a disk partitioning tool. The correct flag is -l (lowercase L), not -1. Even with the correct flag, fdisk -l /dev/sdb1 would only show partition details, not filesystem usage or inode information relevant to the write error.
C. lsblk /dev/sdb1:
This command lists information about block devices in a tree format. It is useful for seeing the device hierarchy (what partitions belong to which disks) but does not provide information about filesystem usage, inodes, or why writes are failing.
D. du -sh /oracle1:
This command estimates the disk space used by files and directories within /oracle1. The df -h output has already shown that only 1% of the disk space is used, so running du would not reveal new information about the cause of the write failure.
Reference:
Linux man-pages project (df): The official documentation explains the -i option for displaying inode information.
A systems administrator is tasked with preventing logins from accounts other than root, while the file /etc/nologin exists. Which of the following PAM modules will accomplish this task?
A.
pam_login.so
B.
pam_access.so
C.
pam_logindef.so
D.
pam_nologin.so
pam_nologin.so
Summary:
The requirement is to prevent user logins (except for root) when the /etc/nologin file exists. This is a standard security feature in Linux that allows an administrator to temporarily disable non-root logins, often for system maintenance. The feature is implemented through a Pluggable Authentication Module (PAM) that checks for the existence of this specific file during the login process.
Correct Option:
D. pam_nologin.so:
This is the specific PAM module designed for this exact purpose. When enabled in the PAM configuration for a service (like login or sshd), it checks for the existence of the /etc/nologin file. If the file exists, it prevents any non-root user from logging in and typically displays the contents of the /etc/nologin file as a message to the user.
Incorrect Options:
A. pam_login.so:
There is no standard PAM module named pam_login.so. This is a distractor.
B. pam_access.so:
This module provides log access control based on user names, host names, and domains, typically configured via /etc/security/access.conf. It is not triggered by the existence of the /etc/nologin file.
C. pam_logindef.so:
This is not a standard PAM module. The logindefs are configuration parameters typically found in /etc/login.defs, but there is no PAM module specifically by this name to enforce the nologin functionality.
Reference:
Linux PAM Documentation (pam_nologin): The official documentation explains that the pam_nologin module prevents users from logging into the system when the file /etc/nologin exists.
A Linux administrator is troubleshooting SSH connection issues from one of the
workstations. When users attempt to log in from the workstation to a server with the IP address 104.21.75.76, they receive the following message:

Which of the following is causing the connectivity issue?
A.
The workstation has the wrong IP settings.
B.
The sshd service is disabled.
C.
The server’s firewall is preventing connections from being made.
D.
The server has an incorrect default gateway configuration.
The server’s firewall is preventing connections from being made.
Summary:
Users are receiving a "Connection timed out" error when trying to SSH to a server. A connection timeout occurs when the client's TCP SYN packet receives no response (SYN-ACK) from the server. The ss output on the server confirms the SSH daemon (sshd) is running and correctly listening on port 22. However, a tcpdump on the server shows no incoming SSH connection attempts when a user tries to connect, which strongly indicates a network filtering device, such as a firewall on the server or an intermediate network device, is blocking the packets before they reach the sshd process.
Correct Option:
C. The server’s firewall is preventing connections from being made:
This is the most direct cause. The evidence shows the service is running (ss -tulpn), but the packets are not reaching it (tcpdump shows no traffic). A local firewall (like iptables or firewalld) on the server is the most common reason for this specific scenario, where the service is up but the packets are blocked.
Incorrect Options:
A. The workstation has the wrong IP settings:
If the workstation had wrong IP settings (like an incorrect default gateway), it would not be able to route packets to the internet at all. The fact that the ping command from the workstation reaches the server and gets a reply proves that basic IP connectivity is functional.
B. The sshd service is disabled:
The ss -tulpn output clearly shows that sshd is listening on :::22 and 0.0.0.0:22, meaning the service is active and running. A disabled service would not be listening on any ports.
D. The server has an incorrect default gateway configuration:
An incorrect default gateway on the server would prevent it from sending responses back to networks outside its own local subnet. Since the server can successfully reply to the ping request from the workstation (which is on a different network, 192.168.1.0/24), its routing and default gateway must be correctly configured.
Reference:
firewalld / iptables Documentation: The official documentation for the common host-based firewalls that would explain how to open a port for a service.
A DevOps engineer needs to download a Git repository from https://git.company.com/admin/project.git. Which of the following commands will achieve this goal?
A.
git clone https://git.company.com/admin/project.git
B.
git checkout https://git.company.com/admin/project.git
C.
git pull https://git.company.com/admin/project.git
D.
git branch https://git.company.com/admin/project.git
git clone https://git.company.com/admin/project.git
Summary:
The engineer needs to create a local copy of a remote Git repository for the first time. This initial action of copying a remote repository to the local machine has a specific command. The command must create a new directory, initialize a local Git repository inside it, and copy the entire commit history and files from the remote source.
Correct Option:
A. git clone https://git.company.com/admin/project.git:
This is the fundamental command for this task. git clone is used to target a remote repository and create a full, independent copy of it on the local machine, including all branches, commits, and history. It is the standard way to "download" a repository to start working on it.
Incorrect Options:
B. git checkout https://git.company.com/admin/project.git:
The git checkout command is used to switch between existing branches or restore files in an already cloned repository. It is not used to create a new local copy from a remote URL.
C. git pull https://git.company.com/admin/project.git:
The git pull command is used to update an existing local repository with new changes from its configured remote repository. It fetches and merges changes. It assumes a local repository already exists and is linked to a remote, which is not the case in this initial download scenario.
D. git branch https://git.company.com/admin/project.git:
The git branch command is used to list, create, or delete branches within an existing local repository. It does not interact with a remote repository URL to download its contents.
Reference:
Git Official Documentation (git-clone): The official documentation states that git clone is used to "clone a repository into a new directory."
Using AD Query, the security gateway connections to the Active Directory Domain
Controllers using what protocol?
A.
Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI)
B.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS)
C.
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
D.
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP)
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
Summary:
AD Query is a feature used by security gateways (like Check Point firewalls) to retrieve user and group information from Microsoft Active Directory. Active Directory is fundamentally a directory service that uses a standardized, cross-platform protocol for querying and modifying directory information. This protocol is designed specifically for accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services over an IP network.
Correct Option:
C. Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP):
This is the correct protocol. Active Directory is an LDAP-compliant directory service. The security gateway uses LDAP (typically on port 389 for unencrypted or STARTTLS, and port 636 for LDAPS) to bind to the Domain Controller and perform queries to resolve usernames, check group membership, and retrieve other directory attributes for the purpose of enforcing identity-based security policies.
Incorrect Options:
A. Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI):
WMI is a Windows-specific infrastructure for management and operational data. While it can be used for scripting and management tasks on Windows systems, it is not the standard or primary protocol that external security gateways use to query Active Directory for user and group information. LDAP is the direct and intended method.
B. Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS):
HTTPS is used for secure web traffic. Active Directory Domain Services do not use HTTPS as their primary query protocol. While some modern web services and APIs (like REST) might interact with AD, the core directory access protocol is LDAP.
D. Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP):
RDP is a proprietary protocol developed by Microsoft that provides a user with a graphical interface to connect to another computer over a network connection. It is used for remote desktop access and has no function in querying directory services.
Reference:
Official Vendor Documentation: The primary reference for this information is the official administration guide for the specific security gateway product (e.g., Check Point Security Gateway). These guides explicitly state that the AD Query feature uses the LDAP protocol to communicate with Active Directory Domain Controllers. This is vendor-specific knowledge relevant to network security appliances.
A Linux engineer has been notified about the possible deletion of logs from the file
/opt/app/logs. The engineer needs to ensure the log file can only be written into without removing previous entries.

Which of the following commands would be BEST to use to accomplish this task?
A.
chattr +a /opt/app/logs
B.
chattr +d /opt/app/logs
C.
chattr +i /opt/app/logs
D.
chattr +c /opt/app/logs
chattr +a /opt/app/logs
Summary:
The requirement is to protect a log file so that new data can be appended (written to the end), but existing data cannot be deleted or overwritten, and the file itself cannot be removed. This calls for a filesystem attribute that enforces append-only mode, which is a common security measure for critical log files to preserve an audit trail.
Correct Option:
A. chattr +a /opt/app/logs:
This is the correct command. The +a flag sets the "append-only" attribute. When this attribute is set, the file can only be opened in append mode for writing. This prevents any existing content from being overwritten or truncated and also prevents the file from being deleted, perfectly meeting the requirement to preserve log history.
Incorrect Options:
B. chattr +d /opt/app/logs:
The +d flag sets the "no dump" attribute, which means the file will be skipped by the dump backup utility. It has no effect on file writing or deletion permissions.
C. chattr +i /opt/app/logs:
The +i flag sets the "immutable" attribute. This is stronger than required; it prevents all modifications to the file, including writing new data (appending). The file becomes completely read-only, which would stop the application from logging altogether.
D. chattr +c /opt/app/logs:
The +c flag enables automatic compression on the filesystem level. The kernel will automatically compress the file as it is written. This does not protect the file from being deleted or overwritten.
Reference:
Linux man-pages project (chattr): The official documentation describes the a attribute, which allows a file to be only opened in append mode for writing.
A Linux administrator is alerted to a storage capacity issue on a server without a specific mount point or directory. Which of the following commands would be MOST helpful for troubleshooting? (Choose two.)
A.
parted
B.
df
C.
mount
D.
du
E.
fdisk
F.
dd
G.
ls
df
D.
du
Summary:
A storage capacity issue has been reported without a specific location, meaning the administrator does not know which filesystem or directory is full. The troubleshooting process requires a two-step approach: first, identifying which mounted filesystem is low on space, and second, drilling down into that filesystem to find which specific files and directories are consuming the most disk space.
Correct Options:
B. df:
This is the most critical first command. The df (disk free) command, especially with the -h flag (df -h), provides a high-level overview of disk space usage for all mounted filesystems. It quickly shows the administrator which specific mount point (e.g., /, /home, /var) is at or near 100% capacity, narrowing down the problem area.
D. du:
Once the full filesystem is identified with df, the du (disk usage) command is used to investigate within that filesystem. Running du -sh /path/to/full/mountpoint/* sorts the subdirectories by size (du -sh /* | sort -h is also very effective), revealing the specific large files or directories responsible for the consumption.
Incorrect Options:
A. parted:
This is a disk partitioning and resizing tool. It is used to manage the partition table on a disk, not to troubleshoot filesystem capacity usage.
C. mount:
This command shows which filesystems are currently mounted and their options, but it does not show how much space is free or used on them.
E. fdisk:
This is a partition table manipulator. Like parted, it is used for managing disk partitions, not for analyzing disk space usage on existing filesystems.
F. dd:
This is a low-level tool for converting and copying files, often used for creating disk images or writing ISO files to USB drives. It is not a tool for diagnosing disk capacity.
G. ls:
The ls command lists directory contents and file names. While ls -lh shows file sizes, it is not efficient for recursively calculating the total size of directories, which is the primary function of du.
Reference:
Official CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Exam Objectives: This scenario falls under Objective 3.2: "Given a scenario, manage storage, files, and directories in a Linux environment," which includes managing disk quotas and file compression. The df and du commands are the fundamental tools for this objective.
A Linux administrator needs to resolve a service that has failed to start. The administrator runs the following command:

Which of the following is MOST likely the issue?
A.
The service does not have permissions to read write the startupfile.
B.
The service startupfile size cannot be 81k.
C.
The service startupfile cannot be owned by root.
D.
The service startupfile should not be owned by the root group.
The service does not have permissions to read write the startupfile.
Summary:
The systemctl status command reveals that the service failed to start and the log snippet shows a "Permission denied" error when trying to open a file. The file in question, /etc/startupfile, is owned by root:root with permissions 640 (rw-r-----). This means only the root user can read and write it, while the root group can only read it. All other users have no access. The service likely runs under a non-root user account that does not have the necessary read permissions for this file.
Correct Option:
A. The service does not have permissions to read the startupfile:
The "Permission denied" error is a direct indicator of this issue. The permissions 640 on a file owned by root:root grant read access only to the root user and members of the root group. If the service process runs as a different user (e.g., a dedicated service account), it will not have read access, causing the failure.
Incorrect Options:
B. The service startupfile size cannot be 81k:
There is no inherent restriction on service file sizes being 81k. This size is perfectly normal for a configuration or startup script and is not the cause of the "Permission denied" error.
C. The service startupfile cannot be owned by root:
It is standard and secure practice for system configuration and startup files in /etc to be owned by the root user. Ownership by root is not the problem; the problem is the lack of read permissions for the specific user context the service runs under.
D. The service startupfile should not be owned by the root group:
While fine-grained group ownership can be used, it is very common for system files in /etc to be owned by the root group. The current group ownership is not inherently wrong. The core issue remains the permissions (640) that exclude the service's user.
Reference:
systemd Official Documentation (System Unit Configuration): While not a direct permissions guide, the documentation emphasizes that services often run as specific users and must have appropriate file access.
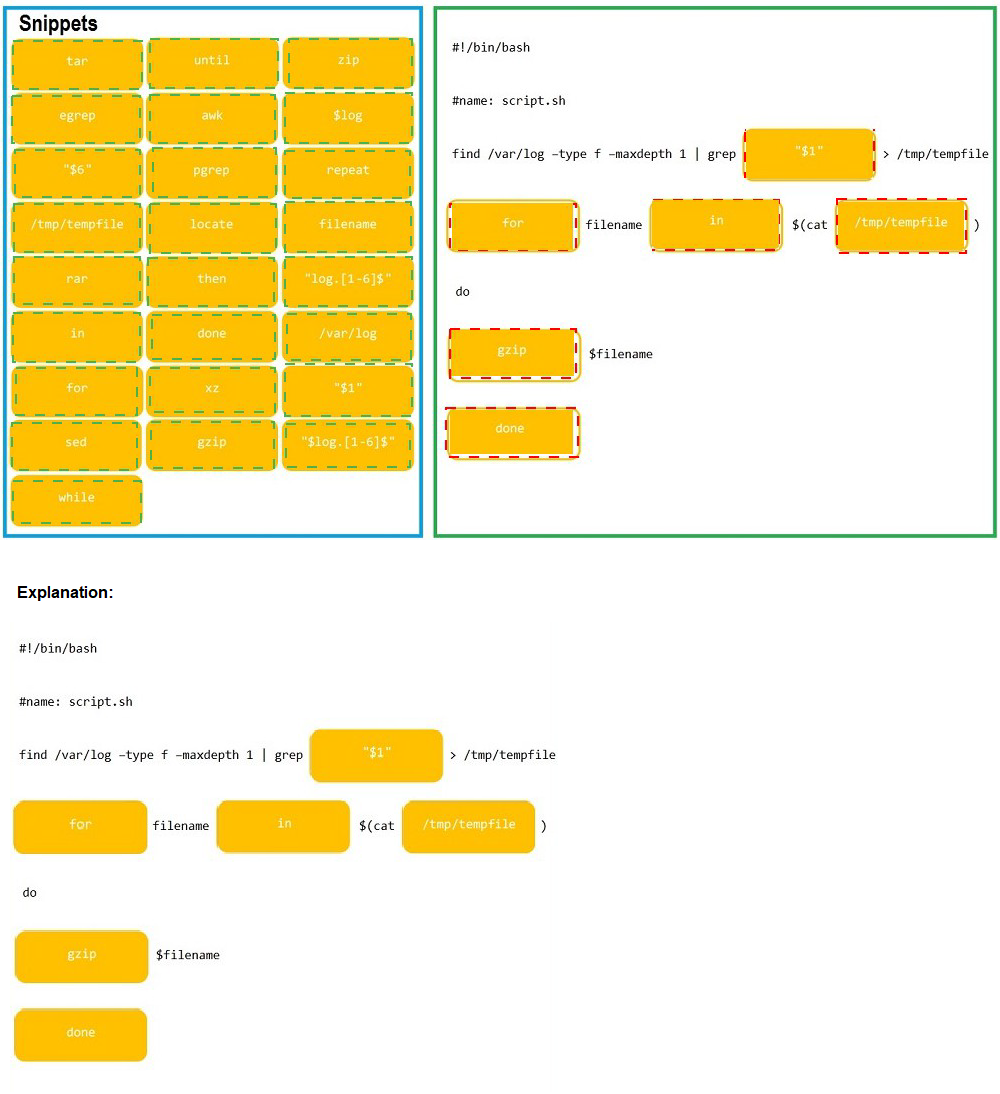
As a Systems Administrator, to reduce disk space, you were tasked to create a shell script that does the following:
Add relevant content to /tmp/script.sh, so that it finds and compresses rotated files in /var/log without recursion.
INSTRUCTIONS
Fill the blanks to build a script that performs the actual compression of rotated log files.
If at any time you would like to bring back the initial state of the simulation, please click the Reset All button.

| Page 16 out of 48 Pages |
| XK0-005 Practice Test | Previous |
