An administrator at a small business notices an increase in support calls from employees who receive a blocked page message after trying to navigate to a spoofed website. Which of the following should the administrator do?
A. Deploy multifactor authentication.
B. Decrease the level of the web filter settings
C. Implement security awareness training.
D. Update the acceptable use policy
Explanation
The scenario describes users attempting to navigate to spoofed websites (fraudulent sites designed to look legitimate) and being blocked by a web filter. This indicates that a technical control (the filter) is working correctly to prevent the threat.
The Root Cause:
The problem is that employees are clicking on links that lead to these malicious sites. This is a human factor issue, not a technical failure.
The Solution:
The most effective and appropriate response is to address this human factor through security awareness training. This training should educate employees on how to:
Identify phishing emails and suspicious links.
Recognize the signs of a spoofed website (e.g., checking the URL for slight misspellings, looking for HTTPS certificates).
Follow proper procedures for reporting suspected phishing attempts.
This proactive measure aims to reduce the number of times users click on malicious links in the first place.
Why the Other Options Are Incorrect
A. Deploy multifactor authentication (MFA):
MFA is a critical security control for protecting accounts from unauthorized access, even if credentials are stolen. However, it does not prevent users from clicking links and attempting to visit spoofed websites. It protects against the consequences of a successful phishing attack but does not address the initial user behavior described.
B. Decrease the level of the web filter settings:
This would be a dangerous and incorrect action. The web filter is successfully doing its job by blocking access to known malicious sites. Lowering its security settings would allow employees to access these spoofed websites, potentially leading to malware infections or credential theft.
D. Update the acceptable use policy (AUP):
An AUP defines proper and improper use of company resources. While it might prohibit visiting malicious sites, updating it is a passive administrative control. It sets rules but does not actively train users to recognize the threat. It also does nothing to address the immediate behavior of clicking links.
Reference
This aligns with the CompTIA Security+ (SY0-701) Exam Objectives, specifically under:
5.5 Explain the importance of human resources security and third-party risk management.
This includes the critical role of security awareness training in creating a human firewall against social engineering and phishing attacks.
Select the appropriate attack and remediation from each drop-down list to label the corresponding attack with its remediation.
INSTRUCTIONS
Not all attacks and remediation actions will be used.
If at any time you would like to bring back the initial state of the simulation, please click the Reset All button.
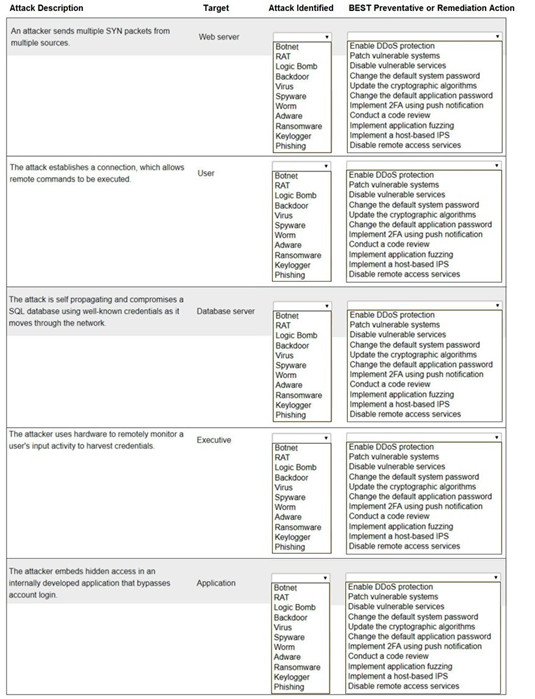
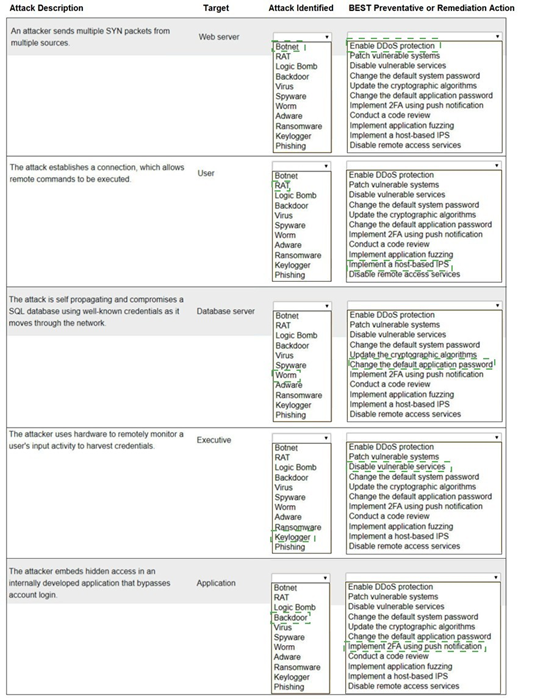
1. An attacker sends multiple SYN packets from multiple sources.
Target: Web server
Attack Identified: This is a DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack, specifically a SYN flood. It is not listed by that exact name, but the remediation gives it away. The closest match in the "Attack Identified" list is not a direct fit, indicating the attack type is implied by the action.
BEST Preventative or Remediation Action: Enable DDoS protection (This action is specifically designed to mitigate large-scale volumetric attacks like SYN floods from multiple sources.)
2. The attack establishes a connection, which allows remote commands to be executed.
Target: User
Attack Identified: RAT (Remote Access Trojan). This malware provides the attacker with remote control of the victim's machine, allowing them to execute commands.
BEST Preventative or Remediation Action: Implement a host-based IPS (A host-based Intrusion Prevention System can detect and block the malicious network traffic and behavior associated with a RAT calling home and receiving commands.)
3. The attack is self propagating and compromises a SQL database using well-known credentials as it moves through the network.
Target: Database server
Attack Identified: Worm (A worm is a self-replicating, self-propagating piece of malware that spreads across a network without user interaction.)
BEST Preventative or Remediation Action: Change the default application password (The attack specifically uses "well-known credentials." The most direct remediation is to change those default passwords on the database service to strong, unique ones, preventing the worm from authenticating.)
4. The attacker uses hardware to remotely monitor a user's input activity to harvest credentials.
Target: Executive
Attack Identified:Keylogger (The term "Keylogger" is not in the list, but Keyfogger is a likely typo or specific brand meant to represent a keylogger. It is hardware or software that records keystrokes to harvest credentials.)
BEST Preventative or Remediation Action: Implement MFA using push notification (Multi-factor authentication using push notifications is the best remediation. Even if credentials are harvested by the keylogger, the attacker would still need to bypass the second factor to gain access.)
5. The attacker embeds hidden access in an internally developed application that bypasses account login.
Target: Application
Attack Identified: Backdoor (A backdoor is a piece of code intentionally hidden in an application to bypass normal authentication mechanisms and provide covert access.)
BEST Preventative or Remediation Action: Conduct a code review (The most effective way to find a maliciously planted backdoor in custom-developed code is through a thorough manual or automated code review by a security-aware developer.)
A software developer would like to ensure. The source code cannot be reverse engineered or debugged. Which of the following should the developer consider?
A. Version control
B. Obfuscation toolkit
C. Code reuse
D. Continuous integration
E. Stored procedures
Explanation
Obfuscation is a technique specifically designed to make source code difficult for humans to understand and for automated tools to reverse-engineer or debug.
How it works:
An obfuscation toolkit will transform the original, readable source code into a functional equivalent that is deliberately complex, confusing, and unstructured. It does this by renaming variables to nonsensical characters, inserting dead code, encrypting parts of the code, and breaking up logical flows.
Purpose:
The primary goal is to protect intellectual property and prevent malicious actors from easily analyzing the code to find vulnerabilities, bypass licensing checks, or create exploits. This directly addresses the developer's goal of preventing reverse engineering and debugging.
Why the Other Options Are Incorrect
A. Version control:
Systems like Git are used to track changes in source code over time, allowing developers to collaborate and revert to previous states. They do not protect the code from being reverse-engineered once it is compiled and distributed.
C. Code reuse:
This is the practice of using existing code to build new functionality. It improves development efficiency but has no effect on the ability to reverse engineer the final application.
D. Continuous integration (CI):
CI is a development practice where developers frequently merge code changes into a central repository, after which automated builds and tests are run. It is a process for improving software quality and speed of development, not for securing code against analysis.
E. Stored procedures:
These are pre-compiled SQL code stored within a database server. They are used to encapsulate database logic for performance and security but are unrelated to protecting application source code from reverse engineering.
Reference
This aligns with the CompTIA Security+ (SY0-701) Exam Objectives, specifically under:
2.1 Explain the importance of security concepts in an enterprise environment.
The concept of obfuscation falls under application security and protecting intellectual property.
Which of the following should a security administrator adhere to when setting up a new set of firewall rules?
A. Disaster recovery plan
B. Incident response procedure
C. Business continuity plan
D. Change management procedure
Explanation
A change management procedure is a formal process used to ensure that modifications to IT systems, such as implementing a new set of firewall rules, are reviewed, approved, tested, and documented before being implemented.
Why it's essential for firewall rules:
Firewall rules are a critical security control. Making changes without a formal process can inadvertently create security holes, cause service outages, or violate compliance requirements.
The Process:
The change management procedure would require the security administrator to:
Submit a request detailing the change, its purpose, and its potential impact.
Get approval from relevant stakeholders (e.g., network team, system owners, management).
Test the changes in a non-production environment.
Schedule the implementation for a specific maintenance window.
Document the new rules for future auditing and reference.
Adhering to this process minimizes risk and ensures stability and security.
Why the Other Options Are Incorrect
A. Disaster recovery plan (DRP):
A DRP focuses on restoring IT systems and operations after a major disaster or outage has occurred. It is a reactive plan, not a procedural guide for making routine configuration changes.
B. Incident response procedure:
This procedure outlines the steps to take when responding to a active security incident (e.g., a breach, malware infection). It is used to contain, eradicate, and recover from an attack. Setting up new firewall rules is a proactive maintenance task, not an incident response action.
C. Business continuity plan (BCP):
A BCP is a broader plan that focuses on maintaining essential business functions during and after a disaster. While related to DRP, it is more about keeping the business running (e.g., using manual processes) and is not a guideline for IT change control.
Reference
This aligns with the CompTIA Security+ (SY0-701) Exam Objectives, specifically under:
1.5 Explain organizational security concepts.
Change Management: The objectives emphasize the importance of a formal change management process to maintain security and avoid unintended outages when modifying systems.
Which of the following provides the details about the terms of a test with a third-party penetration tester?
A. Rules of engagement
B. Supply chain analysis
C. Right to audit clause
D. Due diligence
Explanation
Rules of engagement (RoE) is a formal document that outlines the specific terms, conditions, and guidelines for a penetration test or other security assessment.
Purpose:
It acts as a contract between the organization and the third-party penetration testers, ensuring both parties have a clear, mutual understanding of the test's scope and boundaries.
Details Included:
The RoE typically defines:
Scope
Which systems, networks, and applications are to be tested (and which are off-limits).
Timing:
The authorized dates and times for testing (e.g., during business hours or only after hours).
Methods:
The techniques that are permitted (e.g., social engineering, denial-of-service attacks) and哪些 are forbidden.
Communication:
How and when the testers will communicate findings and status updates.
Legal Protections:
Liability waivers and "get out of jail free" instructions in case the test triggers security alarms.
This document is essential for conducting a safe, legal, and effective penetration test.
Why the Other Options Are Incorrect
B. Supply chain analysis:
This is an assessment of the security risks posed by an organization's vendors and partners. It is a broader risk management activity and does not specify the terms for a specific penetration test.
C. Right to audit clause:
This is a provision commonly found in contracts with third-party vendors. It gives the organization the right to audit the vendor's security controls and compliance. It is about the organization auditing others, not about defining the terms for someone to audit the organization.
D. Due diligence:
This is the process of performing a background investigation or risk assessment before entering into an agreement with a third party (e.g., before hiring a penetration testing firm). It is the research done before the contract and RoE are created, not the document that contains the test's terms.
Reference
This aligns with the CompTIA Security+ (SY0-701) Exam Objectives, specifically under:
1.8 Explain the techniques used in penetration testing.
The objectives cover the planning phase of a penetration test, which includes defining the rules of engagement.
The core concept tested is knowledge of the key documents and planning stages involved in a penetration test, with the Rules of Engagement being the definitive document that governs the test's execution.
A company is developing a business continuity strategy and needs to determine how many staff members would be required to sustain the business in the case of a disruption. Which of the following best describes this step?
A. Capacity planning
B. Redundancy
C. Geographic dispersion
D. Tablet exercise
Explanation
Capacity planning is the process of determining the production capacity and resources (including human resources) needed by an organization to meet changing demands for its products or services.
In the context of Business Continuity Planning (BCP), this involves analyzing the minimum number of personnel with the necessary skills required to maintain critical business operations during a disruption.
The goal is to ensure that the organization has a clear understanding of its staffing requirements to operate at a reduced but functional level, which directly aligns with the scenario of determining "how many staff members would be required to sustain the business."
Why the Other Options Are Incorrect
B. Redundancy:
Redundancy refers to duplicating critical components (e.g., servers, network links) to increase reliability and fault tolerance. While it can include having redundant staff (cross-training), the term itself is broader and more technical. The specific act of calculating the number of staff needed is capacity planning.
C. Geographic dispersion:
This is a strategy of physically separating critical infrastructure or personnel across different locations to mitigate the risk of a single disaster affecting all operations. It is about where staff are located, not determining how many are needed.
D. Tablet exercise:
A tabletop exercise is a discussion-based simulation where team members walk through a scenario to test a plan. It is a method for testing the business continuity plan, not the step for developing the strategy and determining resource requirements.
Reference:
This aligns with the CompTIA Security+ (SY0-701) Exam Objectives, specifically under:
3.4 Explain the importance of resilience and recovery in security architecture.
This objective covers business continuity concepts, and capacity planning is a key component of developing a continuity strategy.
A growing company would like to enhance the ability of its security operations center to detect threats but reduce the amount of manual work required tor the security analysts.
Which of the following would best enable the reduction in manual work?
A. SOAR
B. SIEM
C. MDM
D. DLP
Explanation
SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) is specifically designed to automate and orchestrate security processes. It integrates with various security tools (like a SIEM) to automatically execute standardized workflows in response to specific alerts or triggers. For example, upon detecting a phishing email, a SOAR platform could automatically quarantine the email, disable the affected user account, and create a ticket in the helpdesk system—all without manual intervention from an analyst. This directly reduces the volume of repetitive, manual tasks.
Why the other options are incorrect:
B. SIEM (Security Information and Event Management):
A SIEM is excellent for detecting threats by aggregating and correlating log data from across the network. However, its primary function is alerting and reporting. It identifies the threat but typically requires a security analyst to manually investigate and respond to the alert, which does not inherently reduce manual work.
C. MDM (Mobile Device Management):
MDM is used to manage, monitor, and secure mobile devices (like phones and tablets). It enforces policies (e.g., encryption, app whitelisting) but is a preventive and administrative control, not a tool for automating security analyst workflows in a SOC.
D. DLP (Data Loss Prevention):
DLP tools are designed to prevent the unauthorized exfiltration or exposure of sensitive data. They can block file transfers or alert on policy violations. Like MDM, they are a preventive control and do not automate the broader incident response processes that a SOC analyst would perform.
Reference
This question aligns with the CompTIA Security+ (SY0-701) Exam Objective 4.3: Given an incident, implement appropriate response.
Specifically, it touches on the concept of Automation and Orchestration as key components of a modern security operations center (SOC) to improve efficiency and response times. SOAR is the primary technology that enables this automation.
A software developer released a new application and is distributing application files via the developer's website. Which of the following should the developer post on the website to allow users to verify the integrity of the downloaded files?
A. Hashes
B. Certificates
C. Algorithms
D. Salting
Explanation
The core security principle being tested here is Integrity, one of the three pillars of the CIA Triad (Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability). Integrity ensures that data is accurate, trustworthy, and has not been altered in an unauthorized manner since it was created or sent.
When a user downloads a file from the internet, two major risks exist:
Corruption:
The file could become corrupted during the download process due to a network error, leading to an incomplete or faulty file.
Tampering:
A malicious actor could perform a Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attack, intercept the download, and replace the legitimate application file with a malware-infected version.
To mitigate these risks, users need a reliable method to verify that the file they received is bit-for-bit identical to the file the developer originally posted. This is where the concept of a cryptographic hash comes in.
Why A. Hashes is the Correct Answer
A hash is a cryptographic function that takes an input (like a software file) and produces a unique, fixed-length string of characters, known as a hash value, checksum, or digest.
How it works:
The developer runs the original application file through a secure hashing algorithm (like SHA-256 or SHA-3). This generates a unique alphanumeric string (e.g., a7b33e86...). The developer then posts this hash value prominently on their download page.
How the user verifies integrity:
After downloading the file, the user runs the exact same hashing algorithm on the file they just downloaded. Their local tool (e.g., sha256sum on Linux, PowerShell Get-FileHash on Windows, or a graphical utility) will generate a hash value.
The comparison:
The user compares the hash they generated with the hash posted on the developer's website.
If the hashes match exactly, it is mathematical proof that the downloaded file is identical to the original. Even a change of a single bit in the file would produce a completely different, unpredictable hash value (this is known as the avalanche effect).
If the hashes do not match, the user knows the file is either corrupted or has been tampered with and must not be installed.
This process provides a direct, simple, and highly effective mechanism for users to verify file integrity themselves.
Why the Other Options Are Incorrect
B. Certificates
Purpose:
Certificates are fundamental to Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) and are used for authentication, encryption, and non-repudiation. A developer would use a code signing certificate to cryptographically sign the application file itself.
Why it's not the best answer for integrity:
While a digital signature also guarantees integrity (because it incorporates a hash of the signed code), its primary purpose is to prove authenticity—that the software genuinely came from the claimed developer and not an impostor. The question specifically asks for what to "post on the website to allow users to verify the integrity." The direct method for a user to do this is by comparing hashes. Verifying a certificate signature is a more complex process that involves checking certificate chains and revocation lists, which is handled automatically by the operating system upon installation, not by a user manually checking a website.
C. Algorithms
Purpose:
An algorithm is the mathematical formula or set of rules used to perform an operation, such as creating a hash or encrypting data.
Why it's incorrect:
Simply posting the name of the algorithm (e.g., "We use SHA-256") is useless for verification without the actual output (the hash value). It tells the user how to generate the hash but provides nothing to compare their result to. The user needs the specific hash digest for the specific file to perform the verification.
D. Salting
Purpose:
Salting is a technique used exclusively in the context of password storage.
How it works:
A unique, random string (a "salt") is generated and combined with a user's password before the combination is hashed and stored. The salt is also stored alongside the hash in the database.
Why it's incorrect:
Salting has absolutely no application in file integrity verification. Its sole purpose is to defeat precomputed rainbow table attacks by ensuring that every password hash is unique, even if two users have the same password. Posting a salt for a file download would serve no purpose and is not a standard or relevant practice.
Reference to Exam Objectives
This question directly aligns with the CompTIA Security+ (SY0-701) Exam Objective 2.2: Summarize fundamental cryptographic concepts.
Specifically, it tests your understanding of Cryptographic Hashing, which is defined as "a function that takes a variable-length input and produces a fixed-length output (hash) that represents the original data." The objective emphasizes the properties of hashes that make them ideal for integrity checking:
Deterministic:
The same input always produces the same hash.
Avalanche Effect:
A small change in the input creates a drastic, unpredictable change in the output hash.
Collision Resistant:
It is computationally infeasible to find two different inputs that produce the same hash output.
A company is utilizing an offshore team to help support the finance department. The company wants to keep the data secure by keeping it on a company device but does not want to provide equipment to the offshore team. Which of the following should the company implement to meet this requirement?
A. VDI
B. MDM
C. VPN
D. VPC
Explanation
The core requirement here is a classic cybersecurity challenge: providing secure access to sensitive data and systems for remote users without physically distributing corporate hardware. The finance data is highly sensitive and must remain under the company's control ("on a company device"). The constraint is that the company cannot provide laptops or desktops to the offshore team.
Why A. VDI is the Correct Answer
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) is a perfect solution for this scenario. Here's how it works and why it meets the requirement:
How it works:
VDI hosts desktop operating systems (like Windows 10/11) on centralized servers in the company's data center or cloud. Users (the offshore team) can access these virtual desktops from anywhere using a simple "client" software or even a web browser on their personal, non-corporate devices (e.g., their own laptops).
Meeting the Requirement:
"Keep the data on a company device":
This is the key. With VDI, the actual data and applications never leave the company's servers. The offshore team is not downloading files to their personal laptops; they are only interacting with a visual stream (screen images) of the remote desktop. All processing and data storage happen on the company-controlled hardware in the data center. This significantly reduces the risk of data loss, exfiltration, or infection from an unmanaged personal device.
"Does not want to provide equipment":
The offshore team uses their own existing hardware. The company only needs to provide login credentials and instructions for connecting to the VDI environment. This fulfills the constraint while maintaining security.
In essence, VDI creates a clear separation: the user's personal device is just a dumb terminal for display and input, while all the valuable corporate assets remain securely locked away on company infrastructure.
Why the Other Options Are Incorrect
B. MDM (Mobile Device Management)
Purpose:
MDM is software used to manage, monitor, and secure corporate-owned or employee-owned (BYOD) mobile devices like smartphones and tablets. It enforces policies (passcodes, encryption, app whitelisting) and can remotely wipe devices.
Why it's incorrect:
MDM manages the endpoint device itself. It does not solve the core problem because the sensitive finance data would still need to be present on or accessible from the offshore team's personal devices. The requirement is to avoid this entirely by keeping data on company hardware. MDM would be a complementary security control for the personal devices but is not the primary solution.
C. VPN (Virtual Private Network)
Purpose:
A VPN creates an encrypted tunnel between a remote user's device and the corporate network. It provides secure network-level access as if the user were physically in the office.
Why it's incorrect:
While a VPN provides secure access, it does not satisfy the requirement to keep data on a company device. Once connected via VPN, the user's personal laptop would have full network access and could download, store, and process sensitive finance data directly on its local hard drive. This exposes the data to risks on an unmanaged and potentially insecure device, which is exactly what the company wants to avoid.
D. VPC (Virtual Private Cloud)
Purpose:
A VPC is a private, logically isolated section of a public cloud (like AWS, Azure, or GCP) where you can launch resources (servers, databases) in a virtual network that you define.
Why it's incorrect:
A VPC is infrastructure, not an access solution. It's where you could host your company's servers and applications (including a VDI environment). However, simply having a VPC does not, by itself, provide a method for users to access those resources without data leaving the company's control. You would still need a solution like VDI hosted within the VPC to achieve the desired security outcome. The question is about the access method for users, not the underlying hosting platform.
Reference to Exam Objectives
This question aligns with the CompTIA Security+ (SY0-701) Exam Objective 3.2: Given a scenario, implement secure protocols.
More broadly, it tests your understanding of secure remote access solutions and data security. VDI is a premier technology for enabling secure remote work and implementing a "zero trust" approach by ensuring that sensitive data remains centralized and is never transferred to or executed on untrusted endpoints.
In summary:
VDI is the only technology that allows users on any device to interact with a full desktop environment while ensuring the actual data and applications never leave the security and control of the company's central servers.
A Chief Information Security Officer wants to monitor the company's servers for SQLi attacks and allow for comprehensive investigations if an attack occurs. The company uses SSL decryption to allow traffic monitoring. Which of the following strategies would best accomplish this goal?
A. Logging all NetFlow traffic into a SIEM
B. Deploying network traffic sensors on the same subnet as the servers
C. Logging endpoint and OS-specific security logs
D. Enabling full packet capture for traffic entering and exiting the servers
Explanation
The CISO's goal has two distinct but related parts:
Monitor... for SQLi attacks:
This requires the ability to detect the malicious pattern or signature of a SQL injection attempt in network traffic.
Allow for comprehensive investigations if an attack occurs:
This requires the ability to perform deep, forensic-level analysis after the fact. An investigator needs to see the exact contents of the attack to understand its scope, methodology, and impact.
The additional note that the company uses SSL decryption is critical. It means that even encrypted traffic (HTTPS) can be inspected, eliminating a major blind spot for monitoring.
Why D. Full Packet Capture is the Correct Answer
Full Packet Capture (FPC) involves recording every single bit of data that travels across the network, including all headers and the entire payload of every packet.
Detection:
FPC systems can be integrated with intrusion detection systems (IDS) to scan the captured traffic in real-time for SQLi patterns (e.g., strings like ' OR 1=1--).
Comprehensive Investigation:
This is where FPC shines. If an alert is generated, a security analyst can go back to the exact packet capture from the time of the incident. They can see:
The complete SQL query used in the attack.
The source IP address and port.
The server's exact response (e.g., a database error message or dumped data).
The sequence of the entire attack from start to finish.
This level of detail is invaluable for understanding what the attacker did, what data they may have accessed or exfiltrated, and for providing evidence for remediation and potential legal action. The fact that SSL is decrypted means the contents of these packets are visible and not encrypted.
Why the Other Options Are Incorrect
A. Logging all NetFlow traffic into a SIEM
What it is:
NetFlow is a protocol for collecting metadata about network traffic (e.g., source/destination IP, source/destination port, protocol, amount of data, timestamps).
Why it's insufficient:
NetFlow is excellent for traffic analysis, anomaly detection (e.g., "this server is sending an unusual amount of data to a foreign country"), and high-level monitoring. However, it does not capture the payload (content) of the packets. You might see that a connection was made to the SQL server port (1433, 3306), but you would have no idea what SQL commands were executed. It is useless for detecting the content of a SQLi attack or for conducting a comprehensive forensic investigation into one.
B. Deploying network traffic sensors on the same subnet as the servers
What it is:
This typically refers to placing an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) sensor or a network TAP/SPAN port on the segment where the servers reside.
Why it's insufficient:
While this is a good placement strategy for monitoring, the question is about the strategy or type of data to collect. Simply placing a sensor doesn't specify what it will do. The sensor could be configured for NetFlow (A), packet capture (D), or just simple logging. This option is a means to an end, but it is not the definitive strategy itself. The "what" (packet capture) is more critical than the "where" (same subnet) for this specific goal.
C. Logging endpoint and OS-specific security logs
What it is:
This involves collecting logs from the servers themselves, such as Windows Event Logs, authentication logs, or application-specific logs from the database (e.g., MySQL slow query log, Microsoft SQL Server Audit Logs).
Why it's insufficient:
While extremely valuable for defense-in-depth, this is a reactive and often incomplete method for this specific use case.
Detection:
Database logs are often not monitored in real-time for attack patterns.
Investigation:
The database might only log successful queries or might not log the full details of the connection context (source IP, full payload). If the SQLi attack is successful, it might blind the logging mechanism itself. Most importantly, the goal is to monitor the attack vector (the network traffic), which is the point of entry. Network-based evidence is often more reliable and complete than endpoint logs for understanding the initial attack.
Reference to Exam Objectives
This question aligns with several CompTIA Security+ (SY0-701) Exam Objectives:
Objective 4.4:
Explain the key aspects of digital forensics. Full packet capture is a cornerstone of network forensics, providing the raw evidence needed for an investigation.
Objective 1.4:
Given a scenario, analyze potential indicators of malicious activity. A SQLi attack is a key indicator of malicious activity, and FPC provides the data needed to analyze it.
Objective 4.1:
Given a scenario, analyze indicators of malicious activity. This reinforces the use of tools like FPC to gather data for analysis.
In summary:
While all these options contribute to a robust security posture, only Full Packet Capture (D) provides the complete, unalterable record of network traffic required to both detect the specific content of a SQLi attack and perform a truly comprehensive forensic investigation into it, especially when combined with SSL decryption.
| Page 3 out of 72 Pages |
