The project team determines that software installation can only begin after the desktops have been installed and can be powered on. Which of the following dependencies does this represent?
A. External
B. Internal
C. Mandatory
D. Discretionary
Explanation:
This scenario describes a Mandatory dependency, also known as a hard logic or inherent dependency. This type of dependency is inherent in the nature of the work itself and is physically or legally required.
Why C is correct: The software installation is physically impossible to perform until the desktops (the hardware it runs on) are installed and powered on. This is not a matter of preference or best practice; it is a mandatory, unavoidable sequence of events. You cannot install software on a computer that does not exist or is not operational.
Detailed Analysis of Incorrect Options:
A. External:
An external dependency involves a relationship between a project task and a factor outside the project team's direct control (e.g., a delivery from a vendor, a permit from a government agency). In this case, both the desktop installation and the software installation are tasks within the project's scope and under the team's control.
B. Internal:
An internal dependency is a relationship between two project tasks, both of which are under the project team's control. While this scenario is an internal dependency, the question is asking for the type of logical relationship. "Mandatory" is a more specific and accurate description of the nature of the dependency (it's required), whereas "Internal" simply describes who controls it. "Mandatory" is the best fit.
D. Discretionary:
A discretionary dependency (or preferred logic) is defined by the project team based on best practices, established procedures, or preference. For example, the team might decide to run all unit tests before integration tests as a matter of policy, even though it's not physically mandatory. The dependency described in the question is not discretionary; it is absolutely required.
References:
CompTIA Project+ PK0-005 Exam Objectives:
This question falls under Domain 2.0 "Project Life Cycle Phases," specifically within the scheduling and sequencing of activities. Understanding dependency types is crucial for developing a realistic project schedule.
PMBOK® Guide / Schedule Management: Dependencies are categorized into four types:
Mandatory (Hard Logic): Inherent in the nature of the work.
Discretionary (Soft Logic): Defined by the project team.
External: Involves a relationship between project and non-project activities.
Internal: Involves a precedence relationship between project activities.
The given scenario is a classic example of a Mandatory dependency.
A project manager is currently meeting with a vendor who completed the project work. All invoices associated with the project have been paid. Which of the following best describes the project manager's objective for the vendor meeting?
A. Reassigning resources
B. Removing access
C. Closing contracts
D. Evaluating the project
Explanation:
The scenario describes a project in its final stages: the vendor's work is complete, and all financial obligations (invoices) have been settled. The primary objective of the meeting at this point is to formally conclude the business relationship with the vendor, which is the process of Closing Contracts (also known as contract closure or procurement closure). This involves ensuring all terms of the contract have been met, completing all required paperwork, and obtaining formal sign-off that the contract is complete and closed.
Detailed Analysis of Incorrect Options:
A. Reassigning resources:
This is an internal project team activity. The meeting in question is with an external vendor. The project manager does not reassign the vendor's resources; that is the vendor's internal responsibility.
B. Removing access:
While revoking the vendor's access to systems or facilities might be a specific action item that arises during the contract closure process, it is a tactical step, not the overarching objective of the meeting. The primary goal is the formal administrative and legal closure of the contract itself.
D. Evaluating the project:
Project evaluation is a broader activity that involves assessing the project's overall success against its objectives (scope, time, cost, quality). While the vendor's performance will be evaluated as part of this, the specific meeting with the vendor, especially after all payments are made, is squarely focused on finalizing and closing the contractual agreement.
References:
CompTIA Project+ PK0-005 Exam Objectives:
This question directly aligns with Domain 2.0 "Project Life Cycle Phases," specifically objective 2.5 "Explain the importance of project closure." A key part of project closure is the formal closure of all procurement contracts.
PMBOK® Guide / Project Procurement Management:
The final process in procurement management is "Close Procurements." This process involves completing and settling each contract, including resolution of any open items and formal confirmation that the contract has been fulfilled. The meeting described is a key activity within this process.
A project team member wrote a user guide over the past ten days. Given the following scatter diagram.
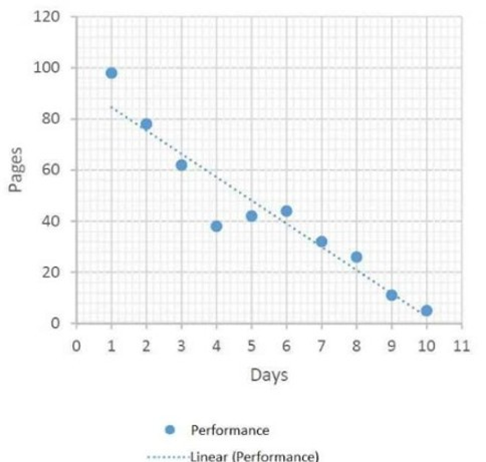
Which erf the following can be formally conducted?
A. The team member prioritized other tasks over the completion of this task
B. The learn member had performance issues over time.
C. There is a negative correlation with 6me and output
D. This is a display of units of outstanding work to predict completion
Explanation:
The scatter diagram shows a clear downward trend in "Performance" as "Days" increase, which is visually reinforced by the downward-sloping linear trendline. This indicates a negative correlation: as one variable (time/days) increases, the other variable (performance/output) tends to decrease.
Detailed Analysis of Incorrect Options:
A. The team member prioritized other tasks over the completion of this task:
This is an assumption about the team member's priorities or work habits. The chart shows performance, not how time was allocated. There is no data provided about other tasks, so this cannot be formally concluded from the scatter diagram alone.
B. The team member had performance issues over time:
While the chart shows declining performance, describing it as "performance issues" is a subjective interpretation. The data formally shows a correlation between time and reduced output, but it does not diagnose the cause (e.g., was it task complexity, motivation, external factors?). "Performance issues" implies a personal deficiency, which the chart data alone cannot support.
D. This is a display of units of outstanding work to predict completion:
This describes a burn-down chart, not a scatter diagram. A burn-down chart shows the remaining work versus time. This chart shows "Performance" (likely output or quality) versus "Days," which is a relationship between two variables, not a depiction of remaining work.
References:
CompTIA Project+ PK0-005 Exam Objectives:
This question falls under Domain 4.0 "Project Tools and Documentation," specifically the use of charts and diagrams for performance analysis. Scatter diagrams are used to identify and correlate relationships between two variables.
Quality Management & Data Analysis:
A scatter diagram is a statistical tool that plots two variables to determine their relationship. The trendline shows the direction of the correlation:
Upward Slope: Positive correlation
Downward Slope: Negative correlation
No Slope: No correlation
A business analyst has gathered information directly from the client and is currently working with the project manager to identify what to include in the document in order to finish it. Which of the following processes should the project manager do next?
A. Validate the scope.
B. Create the work breakdown structure.
C. Define the scope.
D. Collect the requirements.
Explanation:
In this scenario, the business analyst has already gathered information directly from the client, which means the requirements collection phase is complete. The next logical step for the project manager (PM) is to define the scope — that is, to translate the gathered requirements into a clear, detailed scope statement outlining the project’s deliverables, boundaries, assumptions, and acceptance criteria.
The Define Scope process involves creating the project scope statement, which serves as the foundation for all subsequent planning. It describes what work will be done and what will not be done (inclusions and exclusions). This process ensures that both the client and project team have a shared understanding of the deliverables and project objectives.
According to the PMI PMBOK® Guide (7th Edition) and CompTIA Project+ PK0-005 Exam Objectives (Domain 2.1 and 2.2 — Scope Management), the Define Scope process comes after collecting requirements and before creating the work breakdown structure (WBS).
Here’s the correct sequence of scope management processes:
Collect Requirements → Identify stakeholder needs and document them.
Define Scope → Develop the detailed description of the project and product.
Create WBS → Break down deliverables into smaller, manageable work packages.
Validate Scope → Obtain formal acceptance of deliverables from stakeholders.
Since the business analyst has already gathered the requirements, the project manager’s next step is to define the scope — converting the raw requirements into a structured, approved scope statement that will guide the creation of the WBS and overall project plan.
The scope definition ensures that all team members and stakeholders clearly understand the boundaries of the project and prevents scope creep, which is one of the most common risks in project execution.
🚫 Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Validate the scope:
The Validate Scope process occurs later in the project lifecycle, typically during monitoring and controlling, after deliverables are completed or partially completed. It involves obtaining formal acceptance of the completed deliverables from the customer or sponsor. Since the question describes a scenario where the project is still in the planning phase, it’s too early to validate scope. You must first define it
B. Create the work breakdown structure (WBS):
The WBS is developed after the scope statement has been finalized. It breaks down the scope into smaller, manageable components or work packages. However, you cannot create the WBS without first defining the scope, since the WBS is derived directly from the scope statement. Therefore, this step comes after defining the scope, not before.
D. Collect the requirements:
This step has already been performed — the question clearly states that the business analyst has gathered information directly from the client, meaning the requirements collection process is complete. Moving backward to repeat this step would waste time and duplicate effort. The next logical step is to use the collected requirements to define the project scope.
📚 References:
CompTIA Project+ (PK0-005) Exam Objectives, Domain 2.2 — Apply Project Management Processes (Scope, Schedule, and Planning).
PMI PMBOK® Guide, 7th Edition, Scope Management Performance Domain.
CompTIA Project+ Study Guide (PK0-005, Sybex 2024 Edition) — Chapter on Defining Scope and Creating the WBS.
PMI Process Groups Practice Guide, Scope Management: Collect Requirements → Define Scope → Create WBS → Validate Scope.
Summary:
Since the requirements have already been gathered, the project manager’s next task is to define the scope by developing a scope statement that clearly identifies what the project will deliver, its boundaries, and success criteria.
Collect Requirements: Already completed (input gathered by the business analyst).
Define Scope: Next logical step — create the scope statement from those requirements. ✅
Create WBS: Comes after defining the scope.
Validate Scope: Performed after deliverables are completed.
Which of the following is a reason to use a SOW on a project?
A. To find out the contact information for the vendors
B. To review the list of stakeholders
C. To ensure the team stays within the scope of the contract
D. To give explicit instruction on how to execute the work
Explanation:
A Statement of Work (SOW) is a foundational document that formally defines the project's scope, including objectives, deliverables, milestones, and boundaries. Its primary purpose is to serve as a reference point to prevent scope creep and ensure all work performed aligns with the agreed-upon contract. By clearly stating what is in-scope and out-of-scope, the SOW provides the criteria for managing change requests and verifying that the team's work remains within the contractual boundaries.
Detailed Analysis of Incorrect Options:
A. To find out the contact information for the vendors:
This is administrative information that would be contained in a contract or a vendor information sheet, not the primary purpose of an SOW. The SOW focuses on the work to be done, not the contact details.
B. To review the list of stakeholders:
A stakeholder register is the specific document used to identify and analyze stakeholders. While the SOW might mention key parties (like the client and sponsor), its purpose is not to provide a comprehensive stakeholder list.
D. To give explicit instruction on how to execute the work:
The SOW defines what needs to be delivered and the high-level requirements, but it does not typically provide the detailed, step-by-step "how-to" instructions. That level of detail is found in technical design documents, work plans, or the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS). The SOW is about the "what," while the project plan and related documents cover the "how."
References:
CompTIA Project+ PK0-005 Exam Objectives:
This question falls under Domain 2.0 "Project Life Cycle Phases," specifically objective 2.4 "Explain the importance of procurement and vendor selection." The SOW is a critical document in defining procurement scope.
Project Management & Contracting:
The SOW is a key component of the contractual agreement. It is used to ensure both the buyer and the seller (or the project team) have a mutual understanding of the work to be performed, which is essential for controlling scope and avoiding disputes. It is the baseline against which project performance and deliverables are measured.
A stakeholder works in a remote location and has not been replying to emails. The Internet service in that location is intermittent, and the stakeholder prefers to be contacted by telephone. Which of the following artifacts should the project manager have prepared to avoid this situation?
A. Responsibility assignment matrix
B. Acceptable communication channels
C. Risk registry
D. Staff directory
📘 Explanation:
The most relevant artifact to avoid communication breakdowns with remote stakeholders is the acceptable communication channels document. This defines:
Each stakeholder’s preferred method of contact (e.g., phone, email, messaging apps)
Availability constraints (e.g., time zones, connectivity issues)
Backup methods for critical communications
In this scenario, the stakeholder prefers telephone due to unreliable internet. If the project manager had documented and respected this preference, delays and missed updates could have been avoided. This artifact is typically part of the communications management plan and ensures that all parties receive timely, effective communication.
❌ Why other options are incorrect:
A. Responsibility assignment matrix (RAM):
Defines roles and responsibilities, not communication preferences.
C. Risk registry:
Tracks project risks, but doesn’t manage stakeholder communication methods.
D. Staff directory:
Lists contact details, but doesn’t specify how or when to communicate with each person.
🔗 References:
📘 CompTIA Project+ PK0-005 Exam Objectives, Domain 2.3 – “Develop communication management plans”
📘 PMI PMBOK® Guide – Seventh Edition, under “Communications Management” and “Stakeholder Engagement”
📘 PMI Practice Guide for Project Communications Management, Section 3.1 – Communication Preferences and Channels
Which of the following provides a layered approach to logging in to systems that contain an organization's most valuable intellectual property?
A. Remote access
B. Password protection
C. Multifactor authentication
D. Virtual private network
Explanation:
Multifactor authentication (MFA) provides a layered approach to logging in and is the most effective method for protecting systems containing an organization’s most valuable intellectual property.
MFA requires users to provide two or more independent credentials before granting access:
Something you know (e.g., a password or PIN)
Something you have (e.g., a security token, smart card, or mobile app authenticator)
Something you are (e.g., fingerprint, retina scan, or other biometric verification)
This layered approach ensures that even if one factor is compromised (e.g., a stolen password), unauthorized users cannot gain access without the additional factors. For sensitive systems containing intellectual property, MFA significantly reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
According to the CompTIA Security+ and Project+ best practices, MFA is considered one of the most important security controls for safeguarding high-value digital assets. It aligns with the principle of defense-in-depth, which layers multiple security mechanisms to protect critical information.
🚫 Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Remote access:
Remote access is a method that allows users to connect to a system from outside the corporate network. While remote access is often combined with MFA for security, remote access itself does not provide layered authentication. It is simply a pathway into the system and can be exploited if not properly secured.
B. Password protection:
Passwords are a single layer of security. While necessary, relying solely on passwords is increasingly risky because of password theft, phishing, or brute-force attacks. Password protection alone does not provide a layered approach, making it insufficient for highly sensitive systems.
D. Virtual private network (VPN):
A VPN encrypts network traffic between a remote user and the corporate network, protecting data in transit. While it enhances security for connections, a VPN does not control user authentication layers. VPNs ensure secure connectivity but do not verify multiple user factors before granting access to critical systems.
📚 References:
CompTIA Project+ PK0-005 Exam Objectives, Domain 3.4 — Security Controls and Access Management.
CompTIA Security+ Study Guide, SY0-701 (2025 Edition) — Chapter on Authentication Methods and MFA.
NIST Special Publication 800-63B (Digital Identity Guidelines) — Digital Authentication Guidelines for MFA Implementation.
PMI PMBOK® Guide, 7th Edition, Security and Risk Management in Projects.
Summary:
To protect systems containing an organization’s most valuable intellectual property, multifactor authentication (MFA) provides a layered login approach requiring multiple verification factors.
Other options:
Remote access: Only a connection method, not layered authentication.
Password protection: Single factor, easily compromised.
VPN: Secures network traffic, but not layered login.
Which of the following is a capital expense?
A. Building lease
B. Building purchase
C. Building maintenance
D. Building insurance
Explanation:
A capital expense (CapEx) refers to the funds used by a company to acquire, upgrade, and maintain physical assets such as property, buildings, or equipment. These are major, long-term investments that are capitalized on the balance sheet and depreciated over their useful life.
Why B is correct: Purchasing a building is a classic example of a capital expenditure. The building is a long-term asset that provides value to the company for many years. Its cost is not fully expensed in the year of purchase but is instead recorded as an asset and depreciated over time.
Detailed Analysis of Incorrect Options:
A. Building lease:
Lease payments are generally considered operational expenses (OpEx). They are ongoing costs for using an asset without owning it and are fully expensed in the accounting period they are incurred. (Note: Certain long-term finance leases can be treated as capital leases, but a standard operating lease is an OpEx).
C. Building maintenance:
Routine maintenance and repairs are operational expenses. These are costs incurred to keep the asset in its normal operating condition and do not significantly extend its life or increase its value. They are expensed in the period they occur.
D. Building insurance:
Insurance premiums are recurring, periodic costs for risk management. These are considered operational expenses and are deducted from revenue in the year they are paid.
References:
1.CompTIA Project+ PK0-005 Exam Objectives:
This question tests knowledge from Domain 5.0 "Project Governance," specifically related to financial management and understanding different types of costs. Distinguishing between capital and operational expenditures is crucial for project budgeting and justification.
2.Corporate Finance & Accounting:
The fundamental distinction is:
Capital Expenditure (CapEx): Money spent to acquire or improve a long-term asset.
3.Operational Expenditure (OpEx):
Money spent on the day-to-day operations of the company.
A project manager must understand this to correctly categorize project costs and understand the financial impact of a project (e.g., a project proposing a CapEx item like a new server rack versus one that increases OpEx like cloud subscription fees).
A piece of equipment has malfunctioned and is stalling the completion of a deliverable for a project. Which of the following should the project manager do next?
A. Buy a replacement for the faulty equipment.
B. Get the maintenance team to resolve the issue.
C. Escalate the issue to the project sponsor.
D. Rate the severity of the impact the issue has on the project.
Explanation:
When a piece of equipment malfunctions and stalls a deliverable, the first step for a project manager (PM) is to assess the situation and determine the severity of its impact on the project’s schedule, cost, quality, and overall objectives. This ensures that any subsequent actions are informed, prioritized, and proportionate.
Rating the severity involves evaluating:
Criticality of the equipment to completing the deliverable.
Extent of the delay the malfunction causes.
Potential impact on other project tasks that depend on the stalled deliverable.
Cost implications of downtime or alternative solutions.
Once the severity is understood, the PM can determine the appropriate corrective action, whether that involves repair, replacement, escalation, or contingency measures. This step aligns with best practices in issue management, as outlined in CompTIA Project+ PK0-005 Exam Objectives (Domain 3.2 — Project Risk, Issue, and Change Management).
By rating the impact first, the PM ensures that:
Resources are allocated efficiently.
The response matches the urgency and importance of the issue.
Decisions, such as purchasing a replacement or escalating to the sponsor, are justified and documented.
🚫 Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Buy a replacement for the faulty equipment:
Buying a replacement may be necessary, but doing so without first assessing severity can result in wasted time, cost, or unnecessary escalation. If the malfunction is minor or can be quickly repaired, buying new equipment could be inefficient. Assessing severity ensures the PM chooses the most cost-effective and timely solution.
B. Get the maintenance team to resolve the issue:
Engaging the maintenance team is a possible solution, but it is premature without understanding the impact of the malfunction. For instance, if the malfunction causes only a minor delay, maintenance may be sufficient. If the delay is critical, other corrective actions (e.g., expedited replacement or escalation) might be required. Evaluating severity first helps determine whether maintenance alone is enough.
C. Escalate the issue to the project sponsor:
Escalation should be reserved for high-impact issues that cannot be resolved within the project team’s authority. Escalating without assessing severity could unnecessarily involve the sponsor in minor issues, creating inefficiency and administrative overhead. Proper impact assessment ensures escalation is warranted.
📚 References:
CompTIA Project+ (PK0-005) Exam Objectives, Domain 3.2 — Manage Project Risks, Issues, and Changes.
PMI PMBOK® Guide, 7th Edition, Issue Management and Corrective Action Processes.
CompTIA Project+ Study Guide (PK0-005, Sybex 2024 Edition) — Chapter on Issue Identification, Analysis, and Resolution.
Project Management Institute (PMI) – Practice Standard for Project Risk Management — Impact assessment and prioritization of issues.
Summary:
When equipment malfunctions:
Assess the severity of the impact — critical step to prioritize and select the best corrective action. ✅
Based on severity, the PM may then:
Engage the maintenance team for minor issues.
Buy a replacement if the equipment is critical and repair is not timely.
Escalate to the sponsor if the issue threatens the project’s objectives and exceeds the team’s authority.
Which of the following is the most important activity for the project manager during the closure of a project?
A. Obtain project sign-off.
B. Capture lessons learned.
C. Document historical information.
D. Release resources.
Explanation:
While all listed activities are critical during project closure, obtaining formal project sign-off is the most important because it is the definitive act that legally and formally ends the project. This sign-off, typically from the project sponsor or customer, signifies that the project's deliverables have been accepted and that the project has met its objectives as defined in the project charter and scope statement. Without this, the project remains open, resources cannot be formally released, and the organization may remain liable for unmet expectations.
Detailed Analysis of Incorrect Options:
B. Capture lessons learned:
This is a vital activity for organizational process improvement and is a key part of administrative closure. However, it can be conducted even after the project has been formally signed off. Sign-off is the prerequisite for truly closing the project's contractual and formal obligations.
C. Document historical information:
This is part of archiving project documents and is important for future reference and audits. Like lessons learned, it is a crucial administrative task but follows the formal acceptance of the project's final deliverables.
D. Release resources:
Releasing team members, equipment, and budgets is a key step. However, this action is logically dependent on formal sign-off. Prematurely releasing resources before the sponsor has accepted the final product could be problematic if further work is required. Sign-off provides the official authorization to disband the project team.
References:
CompTIA Project+ PK0-005 Exam Objectives:
This question falls under Domain 2.0 "Project Life Cycle Phases," specifically objective 2.5 "Explain the importance of project closure." A primary goal of closure is to obtain final sign-off and acceptance from the sponsor or customer.
PMBOK® Guide / Project Integration Management:
The "Close Project or Phase" process emphasizes obtaining final product, service, or result transition acceptance (sign-off) as a primary activity. This formal acceptance is the trigger for all other closure activities.
| Page 2 out of 37 Pages |
