Two companies successfully merged. Following the merger, a network administrator identified a connection bottleneck. The newly formed company plans to acquire a high-end 40GB switch and redesign the network from a three-tier model to a collapsed core. Which of the following should the administrator do until the new devices are acquired?
A. Implement the FHRP.
B. Configure a route selection metric change.
C. Install a load balancer.
D. Enable link aggregation.
Explanation:
Link aggregation (e.g., LACP, EtherChannel) is the best immediate solution because it:
Combines multiple physical links into a single logical link, increasing bandwidth and reducing bottlenecks.
Provides redundancy (failover if one link fails).
Requires no new hardware (uses existing switches/ports).
This is a temporary fix until the 40Gb switch and collapsed core redesign are implemented.
Why Not the Other Options?
A) Implement FHRP (First Hop Redundancy Protocol)
Incorrect: FHRP (e.g., HSRP, VRRP) ensures gateway redundancy but does not improve bandwidth.
B) Configure a route selection metric change
Incorrect: Adjusting metrics (e.g., OSPF cost) influences traffic routing paths, not bandwidth capacity.
C) Install a load balancer
Incorrect: Load balancers distribute traffic across servers (not switches) and require new hardware.
Reference:
CompTIA Network+ Objective 1.4 (Link Aggregation, LACP)
IEEE 802.1AX (Link Aggregation Standard)
Which of the following best describes the transmission format that occurs at the transport layer over connectionless communication?
A. Datagram
B. Segment
C. Frames
D. Packets
Explanation:
Connectionless communication at the transport layer (e.g., UDP) uses datagrams.
Datagram: A self-contained, independent unit of data with no guaranteed delivery or sequencing.
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is the primary example, used for low-latency, loss-tolerant traffic (e.g., VoIP, DNS).
Why Not the Other Options?
B) Segment
Incorrect: Segments are used in connection-oriented transport protocols (e.g., TCP).
C) Frames
Incorrect: Frames operate at the data link layer (Layer 2) (e.g., Ethernet).
D) Packets
Incorrect: Packets are used at the network layer (Layer 3) (e.g., IP).
Reference:
CompTIA Network+ Objective 1.5 (Transport Layer Protocols)
A network administrator is reviewing a production web server and observes the following
output from the netstat command: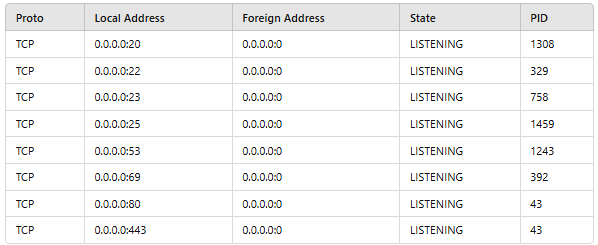
Which of the following actions should the network administrator take to harden the
security of the web server?
A. Disable the unused ports.
B. Enforce access control lists.
C. Perform content filtering.
D. Set up a screened subnet.
Explanation:
The netstat output shows multiple listening TCP ports (20, 22, 23, 25, 53, 69, 80, 443) on the web server, many of which are unnecessary for a typical web server (e.g., FTP port 20, Telnet port 23, SMTP port 25).
Action: Disable unused ports to:
Reduce attack surface (fewer entry points for exploits).
Follow the principle of least functionality (only enable essential services).
Why Not the Other Options?
B) Enforce access control lists (ACLs)
Incorrect: ACLs filter traffic but don’t address the core issue of unnecessary open ports.
C) Perform content filtering
Incorrect: Content filtering blocks malicious web traffic but doesn’t harden the server’s listening services.
D) Set up a screened subnet
Incorrect: A screened subnet (DMZ) isolates public-facing servers but doesn’t fix local port misconfigurations.
Reference:
CompTIA Security+ SY0-601 (Objective 3.3 - Secure Protocols and Hardening)
NIST SP 800-123 (Server Hardening Guidelines)
A network administrator is configuring a new switch and wants to ensure that only assigned devices can connect to the switch. Which of the following should the administrator do?
A. Configure ACLs.
B. Implement a captive portal.
C. Enable port security.
D. Disable unnecessary services.
Explanation:
Port security is the most effective method to ensure only assigned devices can connect to a switch. It works by:
Restricting access based on MAC addresses (statically defined or dynamically learned).
Limiting the number of allowed devices per port.
Taking action (e.g., shutdown, restrict) if unauthorized devices attempt to connect.
Why Not the Other Options?
A) Configure ACLs
Incorrect: ACLs filter traffic by IP/port but do not prevent unauthorized devices from physically connecting.
B) Implement a captive portal
Incorrect: Captive portals are used for web-based authentication (e.g., Wi-Fi hotspots), not switch port access control.
D) Disable unnecessary services
Incorrect: While this hardens the switch, it does not restrict device connections.
Reference:
CompTIA Network+ Objective 4.2 (Port Security)
Cisco Best Practices: Use port security to prevent MAC flooding attacks and unauthorized access.
A network engineer discovers network traffic that is sending confidential information to an unauthorized and unknown destination. Which of the following best describes the cause of this network traffic?
A. Adware
B. Ransomware
C. Darkware
D. Malware
Explanation:
Malware (malicious software) is the broadest and most accurate term for software designed to exfiltrate confidential data to unauthorized destinations. It includes:
Spyware: Secretly collects and transmits data
.
Trojans: Disguised as legitimate software to steal information.
Backdoors: Allows remote unauthorized access.
The scenario describes data exfiltration, a hallmark of malware.
Why Not the Other Options?
A) Adware
Incorrect: Adware displays unwanted ads but does not typically steal data.
B) Ransomware
Incorrect: Ransomware encrypts files for extortion, but doesn’t focus on data exfiltration.
C) Darkware
Incorrect: Darkware refers to tools used in cyberattacks (e.g., exploit kits), not a specific data-theft mechanism.
Reference:
CompTIA Security+ SY0-601 (Objective 1.2 - Malware Types)
MITRE ATT&CK Framework: Data exfiltration tactics (TA0010).
Which of the following provides an opportunity for an on-path attack?
A. Phishing
B. Dumpster diving
C. Evil twin
D. Tailgating
Explanation:
Evil twin is a rogue Wi-Fi access point that mimics a legitimate network, creating an opportunity for an on-path (man-in-the-middle) attack. Attackers can:
Intercept unencrypted traffic (e.g., login credentials).
Redirect users to malicious sites.
This directly fits the definition of an on-path attack, where the attacker secretly relays or alters communications between two parties.
Why Not the Other Options?
A) Phishing
Incorrect: Phishing tricks users into revealing info (e.g., via fake emails), but doesn’t involve real-time traffic interception.
B) Dumpster diving
Incorrect: This is a physical attack (searching trash for sensitive data), unrelated to network traffic
.
D) Tailgating
Incorrect: Tailgating is physical entry (e.g., following someone into a secure area), not a network-based attack.
Reference:
CompTIA Security+ SY0-601 (Objective 1.4 - On-Path Attacks)
NIST SP 800-48 (Wireless Security)
Which of the following network ports is used when a client accesses an SFTP server?
A. 22
B. 80
C. 443
D. 3389
Explanation:
SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol) uses port 22 by default because it operates over the SSH (Secure Shell) protocol, which provides encrypted file transfers.
Unlike regular FTP (ports 20/21), SFTP encrypts both commands and data, making it secure for sensitive transfers.
Why Not the Other Options?
B) 80
Incorrect: Port 80 is for HTTP (unencrypted web traffic).
C) 443
Incorrect: Port 443 is for HTTPS (encrypted web traffic) or sometimes FTPS (FTP over TLS).
D) 3389
Incorrect: Port 3389 is for RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol).
Reference:
CompTIA Network+ Objective 1.5 (Ports and Protocols)
RFC 4251 (SSH Protocol)
A Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of a company purchases a new phone that will be used while traveling to different countries. The CEO needs to be able to place outgoing calls and receive incoming calls on the phone using a SIM card. Which of the following cellular technologies does the CEO's phone need?
A. WDMA
B. CDMA
C. GSM
D. SLA
Explanation:
GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) is the correct choice because:
It uses SIM cards to authenticate users and store subscriber data, allowing the CEO to swap SIMs when traveling internationally.
GSM is the most widely supported cellular standard globally, ensuring compatibility across countries.
Supports both incoming and outgoing calls seamlessly with local carriers.
Why Not the Other Options?
A) WDMA
Incorrect: WDMA (Wavelength Division Multiple Access) is a fiber-optic technology, unrelated to cellular networks.
B) CDMA
Incorrect: CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) is SIM-less in older devices (carrier-locked) and less globally compatible.
D) SLA
Incorrect: SLA (Service Level Agreement) is a contract term, not a cellular technology.
Reference:
CompTIA Network+ Objective 2.4 (Cellular Standards)
GSM vs. CDMA: GSM dominates 90% of the global market (per 3GPP).
Which of the following can be implemented to add an additional layer of security between a corporate network and network management interfaces?
A. Jump box
B. Console server
C. API interface
D. In-band management
Explanation:
Jump box (jump server) is the correct choice because it:
Acts as a secure intermediary (bastion host) between the corporate network and sensitive devices (e.g., switches, routers).
Provides controlled access to management interfaces (SSH, RDP, etc.) while isolating direct connections.
Reduces attack surface by limiting exposure of management interfaces to the corporate network.
Why Not the Other Options?
B) Console server
Incorrect: A console server provides out-of-band (OOB) serial access to devices but doesn’t add a security layer for network-based management interfaces.
C) API interface
Incorrect: APIs enable automation but do not inherently secure management interfaces.
D) In-band management
Incorrect: In-band management uses the production network for device access, which is less secure than a jump box.
Reference:
CompTIA Security+ SY0-601 (Objective 3.3 - Secure Access Controls)
NIST SP 800-53 (AC-17: Remote Access) recommends jump boxes for privileged access.
A user's home mesh wireless network is experiencing latency issues. A technician has:
•Performed a speed test.
- Rebooted the devices.
- Performed a site survey.
- Performed a wireless packet capture.
The technician notices in the packet capture that frames were retransmitted. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the user's network issue?
A. The SSIDs should not be the same.
B. The network has too much overlap.
C. The devices are incompatible with the mesh network.
D. The nodes are underpowered.
Explanation:
Excessive overlap between mesh nodes or neighboring Wi-Fi networks is the most likely cause of:
Frame retransmissions (observed in the packet capture), which occur when signals collide or interfere.
Latency issues, as devices contend for airtime due to overlapping channels or dense node placement.
A site survey would reveal co-channel interference (e.g., multiple nodes on the same channel) or poor channel planning.
Why Not the Other Options?
A) The SSIDs should not be the same
Incorrect: Mesh networks require the same SSID for seamless roaming. Mismatched SSIDs would cause disconnections, not latency.
C) The devices are incompatible with the mesh network
Incorrect: Incompatibility would cause connection failures, not retransmissions or latency.
D) The nodes are underpowered
Incorrect: Underpowered nodes might have weak signals, but retransmissions are more typical of interference/overlap.
Reference:
CompTIA Network+ Objective 2.4 (Wireless Interference and Optimization)
Solution: Adjust node placement, use non-overlapping channels (e.g., 1, 6, 11 for 2.4GHz), or reduce transmit power.
| Page 12 out of 43 Pages |
